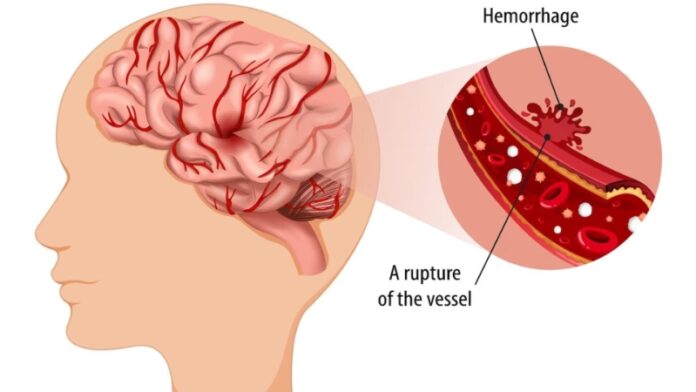
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding (hemorrhage) in or around the brain. This type of stroke can cause significant brain damage and is a medical emergency.
Symptoms
- Sudden severe headache: Often described as the worst headache ever experienced.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness or numbness: Usually affecting one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Vision problems: Double vision, blurred vision, or loss of vision.
- Seizures
- Confusion or altered level of consciousness
- Stiff neck (if the bleeding is in the area surrounding the brain)
Causes
Hemorrhagic strokes are primarily caused by:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): The leading cause of hemorrhagic strokes.
- Aneurysms: Weakened spots in blood vessel walls that can burst.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Abnormal tangles of blood vessels.
- Head trauma: Injury to the head can lead to bleeding in the brain.
- Blood disorders: Conditions like hemophilia or sickle cell anemia that affect blood clotting.
- Blood-thinning medications: Anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Liver disease: Can affect blood clotting mechanisms.
- Drug use: Especially cocaine and amphetamines, which can increase blood pressure.
Treatment
Immediate medical treatment is crucial for hemorrhagic stroke and often involves:
- Emergency Measures:
- Stabilizing the patient: Ensuring proper breathing, circulation, and addressing any life-threatening conditions.
- Controlling bleeding: Reducing or stopping the bleeding in the brain.
- Lowering intracranial pressure: Using medications or procedures to relieve pressure within the skull.
- Medications:
- Anti-hypertensive drugs: To lower blood pressure.
- Anticonvulsants: To prevent or treat seizures.
- Reversal agents: For those on blood thinners, medications to reverse the effects.
- Surgery:
- Aneurysm clipping: Surgically placing a clip on the neck of the aneurysm.
- Coiling (endovascular embolization): Inserting coils into the aneurysm to block blood flow and promote clotting.
- Surgical removal of AVMs: Removing the abnormal tangles of blood vessels.
- Decompressive craniotomy: Removing part of the skull to relieve pressure on the brain.
- Rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy: To regain motor skills and strength.
- Occupational therapy: To improve daily living skills.
- Speech therapy: For those with speech and language difficulties.
- Psychological support: To address emotional and cognitive challenges.
Prevention
Preventing a hemorrhagic stroke involves managing risk factors and making lifestyle changes:
- Control Blood Pressure:
- Regular monitoring and management of hypertension with medications and lifestyle changes.
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Keeping within recommended limits.
- Quit smoking: Avoiding tobacco use.
- Manage Chronic Conditions:
- Effective management of diabetes, high cholesterol, and other health conditions.
- Avoid Drug Abuse:
- Steering clear of recreational drugs, particularly stimulants like cocaine and amphetamines.
- Safety Measures:
- Using protective gear and taking precautions to prevent head injuries.
- Regular Medical Checkups:
- Routine health screenings and checkups to monitor and manage health conditions.
Recognizing the signs of a stroke and seeking immediate medical attention can significantly improve outcomes. Always call emergency services if a stroke is suspected.