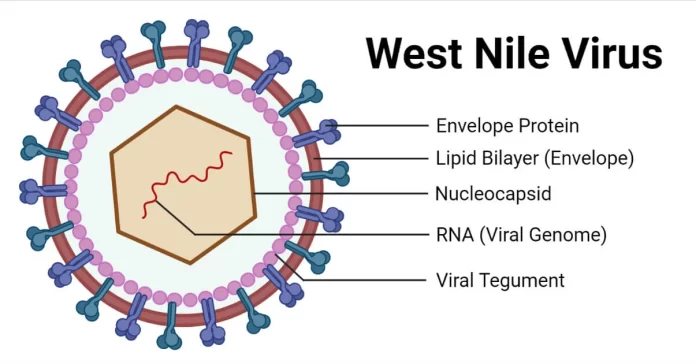
West Nile Virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause illness ranging from mild to severe. Here’s an overview of its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms:
- Mild Symptoms:
- Fever
- Headache
- Body aches
- Fatigue
- Skin rash (occasionally)
- Severe Symptoms (Neuroinvasive Disease):
- High fever
- Stiff neck0
- Disorientation or confusion
- Tremors or muscle weakness
- Severe headache
- Paralysis
- Coma
- Sometimes death
Causes:
- Transmission: Primarily transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes, which pick up the virus by feeding on infected birds.
- Reservoir: Birds act as reservoir hosts for the virus. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds.
Treatment:
- No Specific Treatment: There is no specific antiviral treatment for WNV infection. Treatment is typically supportive and focused on relieving symptoms.
- Hospitalization: Severe cases may require hospitalization for supportive care, including intravenous fluids, respiratory support, and prevention of secondary infections.
Prevention:
- Mosquito Control:
- Reduce mosquito breeding sites by eliminating standing water where mosquitoes lay eggs.
- Use insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus when outdoors.
- Wear long sleeves and pants during peak mosquito activity times.
- Protective Measures:
- Install or repair window and door screens to keep mosquitoes outside.
- Use mosquito netting over cribs, strollers, and outdoor seating areas.
- Avoid outdoor activities during dusk and dawn when mosquitoes are most active.
- Community Efforts:
- Community-wide mosquito control programs can reduce mosquito populations and lower the risk of WNV transmission.
- Surveillance of bird populations can help monitor the spread of the virus and inform control efforts.
- Vaccines: Currently, there is no vaccine available for humans, but research is ongoing in this area.
- Blood Safety: Blood donations are screened for WNV to prevent transmission through blood transfusions.
Conclusion:
West Nile Virus is a significant public health concern, particularly during mosquito season in affected regions. While most people infected with WNV experience mild symptoms or none at all, severe cases can lead to neurological complications or death. Prevention efforts, such as mosquito control measures and personal protection strategies, are crucial for reducing the risk of WNV infection.