The condition known as oral thrush, or oral candidiasis, is caused by an accumulation of the fungus Candida albicans on the oral mucosa. Although candida is a common oral microorganism, it occasionally overgrows and manifests symptoms.
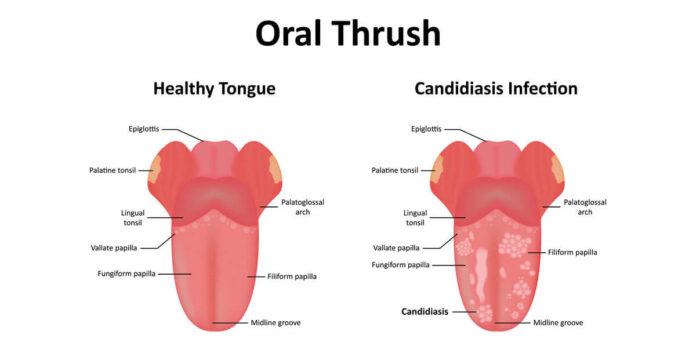
Creamy white lesions, typically on the inner cheeks or tongue, are the result of oral thrush. Oral thrush can occasionally spread to the back of the throat, the tonsils, gums, or roof of the mouth.
While anyone can get oral thrush, those with weakened immune systems, such as babies and elderly adults, those taking certain medications, and those with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to the condition. If you’re healthy, oral thrush is a minor issue; however, if your immune system is compromised, your symptoms might be more severe and challenging to manage.
Signs and symptoms
Both kids and adults
At first, oral thrush symptoms might go unnoticed. Among the symptoms and indicators are:
- Creamy white lesions on the tonsils, inside cheeks, roof of the mouth, and occasionally on the gums and tongue
- cottage cheese-like lesions that are slightly elevated
- redness, burning, or soreness that could be so bad that it makes it hard to swallow or eat
- slight bleeding in the event that you scrape or rub the lesions
- redness and cracking at the mouth’s corners
- a feeling of cottoniness in your mouth
- taste loss
- denture stomatitis, or redness, irritation, and pain under dentures
Severe cases, typically associated with HIV/AIDS-related immune system weakness or cancer, can cause the lesions to spread down your oesophagus, which is a long, muscular tube that runs from the back of your mouth to your stomach (Candida esophagitis). If this happens, you might feel like food is getting stuck in your throat, have pain when swallowing, and have trouble swallowing.
Young children and nursing mothers
Not only do newborns have characteristic white mouth lesions, but they can also be fussy, irritable, and have difficulty feeding. Breastfeeding mothers can contract the infection from them. Then, the infection might move from the baby’s mouth to the mother’s breasts.
The following indications and symptoms may be present in women with a candida infection in their breasts:
- Areola that is unusually sensitive, red, cracked, or itchy
- Skin that is shiny or flaky in the darker, circular region surrounding the areola
- Unusual discomfort while nursing or uncomfortable nipples in between feedings
- Deep-seated stabbing pains in the breast
Causes
In a normal state, your immune system balances the “good” and “bad” microbes that live in your body by warding off harmful invaders like viruses, bacteria, and fungus. However, occasionally these defences falter, which raises the candida fungus population and permits the development of an oral thrush infection.
Candida albicans is the most prevalent type of candida fungus. Your risk of oral thrush can be elevated by a number of factors, including a compromised immune system.
Prevention
By taking these steps, you may be able to lower your risk of getting candida infections:
- Wash your mouth. After taking your medication, make sure to brush your teeth or rinse your mouth with water if you need to use a corticosteroid inhaler.
- Make sure to floss every day or as frequently as your dentist advises, and brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Examine your dentures. Take out your dentures at bedtime. Verify that dentures are comfortable and well-fitting. Make sure your dentures are clean every day. Find out from your dentist how to clean the particular type of dentures you have.
- See your dentist on a regular basis, particularly if you wear dentures or have diabetes. Find out how frequently you need to see your dentist.
- Keep an eye on your diet. Try cutting back on the quantity of meals that contain sugar. These could promote the spread of candida.
- If you have diabetes, make sure your blood sugar is under control. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels can lower salivary sugar levels, which will inhibit the growth of candida.
- A vaginal yeast infection should be treated as soon as possible.
- Take care of your dry mouth. Find out from your doctor how to prevent or cure dry mouth.






















![Introduction to SAP Analytics Cloud [Edition 1]- (FGT-KBA) fugentex logo](https://fugentimes.news/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/fugentex-logo-200x150.jpeg)






