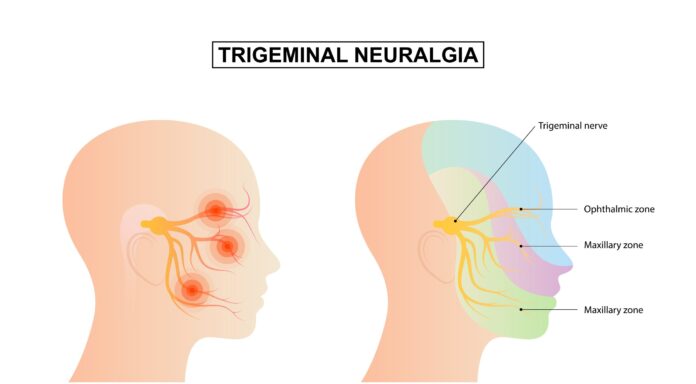
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, one of the major nerves responsible for sensation in the face. This condition is characterized by sudden, severe, and stabbing facial pain, often described as electric shock-like or shooting in nature. The pain is typically experienced on one side of the face and can be triggered by various stimuli, such as touch, eating, or even exposure to wind.
Symptoms:
Sudden, Intense Pain:
- Episodes of severe, stabbing pain.
- Typically unilateral (on one side of the face).
Trigger Factors:
- Touching the face.
- Chewing or talking.
- Exposure to cold wind.
- Brushing teeth or putting on makeup.
Episodic Nature:
- Pain attacks may last from a few seconds to a couple of minutes.
- Episodes can be frequent and unpredictable.
Causes:
The exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia is often unknown, but it is thought to involve compression or irritation of the trigeminal nerve, which may be caused by:
- Blood vessels pressing on the nerve.
- Tumor compressing the nerve.
- Aging-related changes in the nerve.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is based on a thorough medical history, a description of symptoms, and sometimes imaging studies such as an MRI to rule out structural issues or tumors.
Treatment:
Medications:
- Anticonvulsant medications (e.g., carbamazepine) to help control nerve impulses.
- Muscle relaxants.
Surgical Interventions:
- Microvascular decompression: Relieving pressure on the trigeminal nerve by repositioning blood vessels.
- Gamma Knife radiosurgery: Precise radiation to target the trigeminal nerve.
Nerve Blocks:
- Injection of anesthetic agents to numb or block the trigeminal nerve.
Physical Therapy:
- Techniques to improve facial muscle coordination and reduce triggers.
Prevention:
- Avoiding triggers that provoke pain episodes.
- Proper oral hygiene to prevent triggers during tooth brushing.
Complications: Trigeminal neuralgia does not typically lead to serious complications, but the impact on the individual’s quality of life can be substantial due to the intensity and unpredictability of the pain.
Note: Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic condition that often requires long-term management. Individuals experiencing symptoms should seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and to explore appropriate treatment options based on the severity and impact of their symptoms.