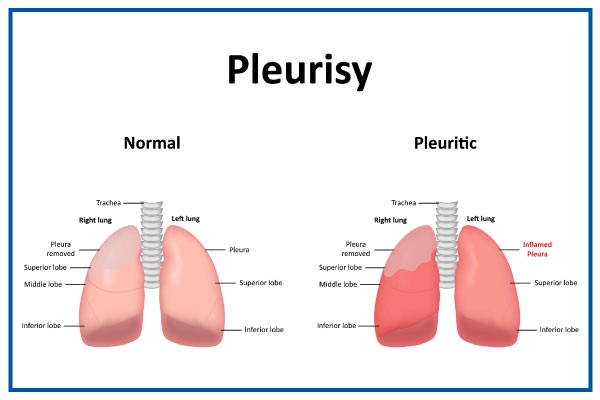
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is an inflammation of the pleura, the double-layered membrane surrounding the lungs and lining the chest cavity. The pleura helps facilitate smooth lung movement during breathing by producing a small amount of fluid.
Symptoms:
- Sharp Chest Pain: Pleuritic chest pain is a hallmark symptom, often exacerbated by breathing or coughing.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or shallow breaths may occur.
- Dry Cough: Some individuals may experience a dry, hacking cough.
- Fever and Chills: Infections causing pleurisy may lead to fever and chills.
- Rapid Breathing: Increased respiratory rate may be observed.
Causes:
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections affecting the respiratory system.
- Pulmonary Embolism: Blood clot in the lungs can cause pleuritic pain.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
- Chest Trauma: Injuries to the chest, rib fractures, or surgery.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs may cause pleurisy as a side effect.
Treatment:
- Addressing Underlying Cause: Treatments depend on the underlying cause, such as antibiotics for infections or anticoagulants for pulmonary embolism.
- Pain Management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
- Corticosteroids: In cases of autoimmune-related pleurisy.
- Thoracentesis: Removal of excess fluid from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
- Supportive Care: Rest, adequate hydration, and management of associated symptoms.
Prevention:
- Vaccinations: Ensure up-to-date vaccinations, especially for influenza and pneumonia.
- Good Respiratory Hygiene: Practice measures to prevent respiratory infections, such as hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with sick individuals.
- Trauma Prevention: Take precautions to avoid chest injuries and trauma.
- Regular Exercise: Maintain overall health and lung function through regular exercise.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: For individuals with autoimmune diseases, managing the underlying condition can reduce the risk of pleurisy.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on individual circumstances.