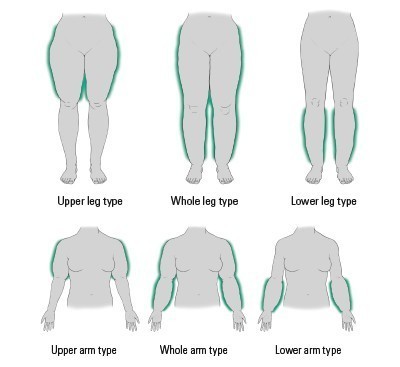
Lipoedema is a chronic condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat cells, primarily in the lower body, such as the hips, thighs, buttocks, and sometimes the arms. It predominantly affects women and often begins or worsens during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. Lipoedema can cause pain, tenderness, swelling, and easy bruising in the affected areas. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Symptoms:
- Enlarged, Disproportionate Fat Deposits: Lipoedema typically manifests as bilateral, symmetrical enlargement of fat cells in the lower body, which may give the appearance of column-like legs or a pear-shaped body.
- Tenderness and Pain: Individuals with lipoedema may experience tenderness or pain in the affected areas, especially upon pressure or touch.
- Swelling and Fluid Retention: Swelling, also known as edema, can occur due to the buildup of fluid in the affected tissues, leading to discomfort and heaviness.
- Easy Bruising: It can cause increased vulnerability to bruising even from minor trauma due to the fragility of blood vessels in the affected areas.
- Diminished Mobility: In advanced stages, lipoedema may impair mobility and lead to functional limitations in daily activities.
Causes:
The exact cause of lipoedema remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to its development, including:
- Hormonal Influence: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly estrogen, may play a role in the pathogenesis of lipoedema, as it predominantly affects women and often worsens during hormonal transitions such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
- Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence suggesting a genetic predisposition to lipoedema, with a familial tendency observed in many cases.
- Vascular and Lymphatic Dysfunction: Dysfunction in the lymphatic and vascular systems may contribute to the abnormal accumulation of fat cells and fluid retention characteristic of lipoedema.
Prevention:
Preventive measures for lipoedema focus on managing symptoms and minimizing its progression. While it may not be possible to prevent lipoedema entirely, the following strategies may help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing weight can help prevent exacerbation of symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Compression Therapy: Wearing compression garments or bandages can help reduce swelling and discomfort associated with lipoedema by supporting the affected tissues and promoting lymphatic drainage.
- Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and manual lymphatic drainage techniques prescribed by a qualified physical therapist can improve circulation, reduce swelling, and enhance mobility.
- Medical Management: Consultation with healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, vascular specialists, and lymphedema therapists, can facilitate personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, which may include medications, surgical interventions, or specialized therapies.
In conclusion, lipoedema is a chronic condition characterized by abnormal fat accumulation primarily in the lower body, causing symptoms such as swelling, tenderness, and pain. While its exact cause remains unclear, factors such as hormonal influence and genetic predisposition may contribute to its development. Preventive measures focus on managing symptoms and may include lifestyle modifications, compression therapy, physical therapy, and medical management tailored to individual needs. Early diagnosis and comprehensive management are essential for optimizing outcomes and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by lipoedema.