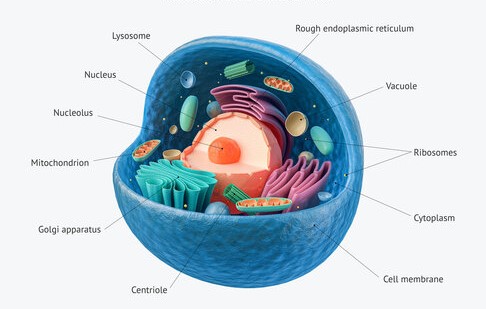
Nucleus-
- Nucleus is the most important cell organelle which directs and controls all its cellular activities.
- It is called as ‘Headquarter of the cell or controller of cell’.
- It was discovered by Robert Brown in 1831.
- In Eukaryotes, a well-defined nucleus is present while in Prokaryotes, a well- defined nucleus is absent.
- Prokaryotes contain a primitive nucleus called Nucleoid.
- It has double layered covering called as nuclear membrane.
- Nuclear membrane has pores which regulate the movement of materials in & out of the Nucleus.
- Besides nuclear membrane, nucleus also contains nucleolus and chromatin material. Chromatin is made up of DNA and Protein, that ultimately condense and forms chromosome.
- Chromosomes or chromatin material consists of DNA which stores and transmits hereditary information for the cell to function, grow and reproduce.
Functions of Nucleus-
- It controls all the metabolic activities cell and regulates the cell cycle.
- It helps in transmission of hereditary characters from parents to their off springs.
Cytoplasm-
- Cytoplasm was discovered by Kolliker in 1862. It is the site of both biosynthetic and catabolic pathways (Metabolic activities)
- It can be divided into two parts –
- Cytosol – Aqueous soluble part contains various fibrous proteins forming cytoskeleton. It contains about 90% water, 7% Protein 2% carbohydrates & 1% etc.
- Cell organelles – Living part of the cells having definite shape, structure and function bounded by plasma membrane. These are single membrane bound, double membrane bound and non-membrane bound Cell organelles.
Endoplasmic Reticulum –
It is the network of membrane bound tubules and sheet present in the cytoplasm. It was discovered by Porter, Claude and Fullam. These are present in all cells except prokaryotes and mammalian erythrocytes.
Endoplasmic reticulum is of two types –
Smooth ER –
- Made of tubules mainly.
- Helps in steroid, lipids and Polysaccharide synthesis.
- Ribosomes are absent.
Rough ER –
- Made of Cisternae and vesicles.
- Helps in protein synthesis.
- Contains ribosome on its surface.
Function of ER –
- It is the only organelle which serves as a channel for the transport of materials between various regions of cytoplasm and between cytoplasm and nucleus.
- It also functions as a cytoplasmic framework to provide surface for some of the biochemical activities. It forms endoskeleton of cell.
- It helps in synthesis of fats, protein, steroids, cholesterol etc.
- SER plays a crucial role in detoxify cation of drugs and poisonous by products.
- Membrane biogenesis: Protein & Lipids produced by ER are used to produce cell membrane.
Golgi apparatus –
Golgi apparatus consists of a system of membrane bounded fluid filled vesicles arranged parallel to each other in stacks called Cisternae along with some large and spherical vesicles. It was discovered by Camillo Golgi. It is absent in prokaryotes, mammalian RBC’s & sieve cells.
Functions of Golgi apparatus –
- Its function includes the storage, modification, Packaging & secretion of products in vesicles.
- It involved in the formation of lysosomes.
- It is secretary in nature.
- It helps in melanin synthesis.
- It also involved in the synthesis of cell wall & plasma membrane.
Mitochondria –
- It is a rod-shaped structure found in cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBC’s.
- These are also absent in prokaryotes.
- It was first seen by Kolliker in insect cells in 1880.
- It is also called as ‘Power House of the Cell’ or the ‘Storage Battery’.
- It is double membranous structure where outer membrane has specific proteins while the inner membrane is folded inside to form chambers called Cristae.
- Mitochondria has its own DNA & Ribosomes
Functions of Mitochondria –
- Its main function is to produce, store and release the energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
- It is the site for cellular respiration (Kreb cycle) in which ATPase produced.
Ribosomes –
- Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis.
- All structural and functional proteins (enzymes) coded by the nuclear DNA are synthesized upon cytoplasmic ribosomes. The DNA codes are transcripted into messenger RNA (MRNA) molecules, which comes out of the Nucleolus and translated (Protein synthesis) by ribosomes attached to RER in the form of proteins.
Functions of Ribosomes –
Ribosomes are the main site of protein synthesis. Synthesized proteins is transported by endoplasmic reticulum.
Plastids –
- It is double membranous, discoidal structure, found mainly in algae and plant cells.
- Besides being discoidal or rhombic in plant cells, they occur in variable shapes like in (algae.) They can be ‘U’- shaped, spiral, coiled, ribbon- shaped etc.
Vacuoles –
- These are membrane bounded regions in the cytoplasm containing water and other substances.
- They are bounded by a single membrane called Tonoplast.
- In animal cells vacuoles are absent or smaller in size. In plant cells a single large vacuole is found which occupies about 90% of the volume of cell.
Functions of Vacuoles –
It helps in maintaining osmotic pressure in a cell & stores toxic metabolic products (waste product, water, sugar, protein etc.) of plant cell.
Lysosome (Suicidal Bag) –
- They are tiny membrane bound cell organelle containing powerful digestive enzymes for intracellular digestion.
- Lysosome are absent in RBC’s
- Lysosomes are synthesised by golgi body & enzymes present in it are synthesised by RER.
Functions –
- Their main function is phagy (digestion). Means they breakdown worn out cell parts.
- They are kind of waste disposal system of the cell.
- They help in digesting foreign materials like invading viruses and bacteria in the cell.
During disturbances in cellular metabolism (i.e., in case of cell damage), lysosomes burst and their enzymes are released into the cytoplasm which digest their own cell. So, they are also called ‘Suicidal Bags’.
Cell Division –
New cells are formed in organisms in order to grow, to replace old, dead and injured cells, and to form gametes required for reproduction. The process by which new cells are made is called cell division. The are two main types of cell division:
- Mitosis –
The process of cell division by which most of the cells divide for the growth is called mitosis. In this process, each cell called mother cell divides to form two identical daughter cells. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as mother cell. It helps in growth and repair of tissues in organisms.
- Meiosis –
Specific cells of reproductive organs or tissues in animals and plants divide to form gametes, which after fertilisation give rise to off spring. They divide by a different process called meiosis which involves two consecutive divisions. When a cell divides by meiosis it produces four new cells instead of just two. These new cells have only half the number of chromosomes than that of the mother cell.