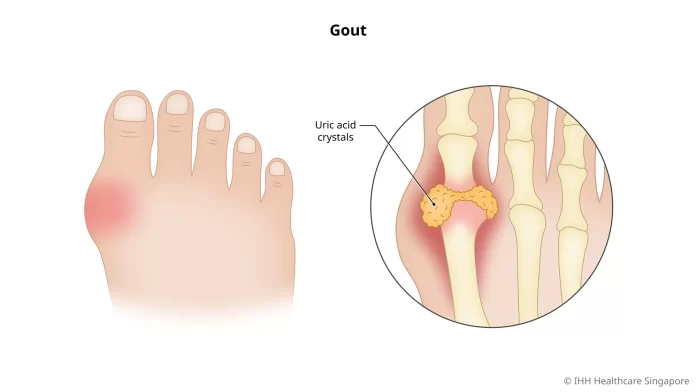
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Here’s an overview of its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms:
- Intense Joint Pain: Typically affects the big toe, but can also occur in other joints like ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
- Swelling: Inflamed joints become swollen, tender, and red.
- Limited Movement: Pain and swelling can restrict joint movement.
- Recurrent Attacks: Gout often manifests in sudden, severe attacks followed by periods of remission.
Causes:
- Uric Acid Buildup: Gout occurs when uric acid accumulates in the blood, forming sharp crystals in the joints.
- Risk Factors: Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing gout, including genetics, diet (high in purines), obesity, certain medications, and medical conditions like high blood pressure or kidney disease.
Treatment:
- Medications:
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): Reduce pain and inflammation during gout attacks.
- Colchicine: Also helps to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Prescribed for severe gout cases.
- Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors (Allopurinol, Febuxostat): Lower uric acid levels by inhibiting its production.
- Probenecid: Helps the kidneys eliminate uric acid.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Modifications: Limit intake of purine-rich foods (e.g., red meat, organ meats, seafood), alcohol, and sugary beverages.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out uric acid.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce uric acid levels and lower the risk of gout attacks.
Prevention:
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy while reducing intake of purine-rich foods and alcohol.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink enough water to promote uric acid excretion.
- Limit Alcohol: Especially beer and spirits, as they can increase uric acid production.
- Regular Exercise: Helps maintain a healthy weight and may lower uric acid levels.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed medications to manage gout, take them as directed to prevent flare-ups.