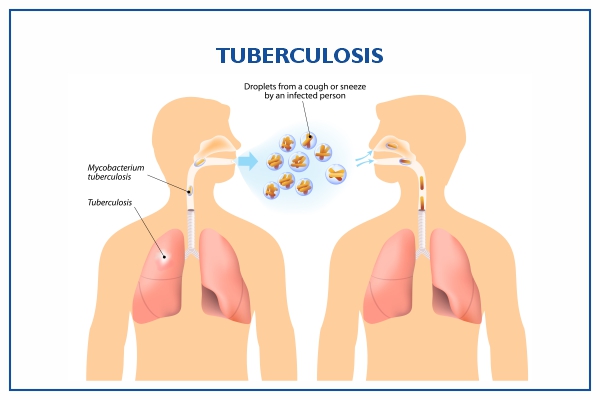
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from person to person through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.
Once rare in developed countries, tuberculosis infections began increasing in 1985, partly because of the emergence of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. HIV weakens a person’s immune system, so it can’t fight the TB germs. In the United States, because of stronger control programs, tuberculosis began to decrease again in 1993. But it remains a concern.
Symptoms
Although your body can harbor the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, your immune system usually can prevent you from becoming sick. For this reason, doctors make a distinction between:
- Latent TB. You have a TB infection, but the bacteria in your body are inactive and cause no symptoms. Latent TB, also called inactive TB or TB infection, isn’t contagious. Latent TB can turn into active TB, so treatment is important.
- Active TB. Also called TB disease, this condition makes you sick and, in most cases, can spread to others. It can occur weeks or years after infection with the TB bacteria.
Signs and symptoms of active TB include:
- Coughing for three or more weeks
- Coughing up blood or mucus
- Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Chills
- Loss of appetite
Causes
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria that spread from person to person through microscopic droplets released into the air. This can happen when someone with the untreated, active form of tuberculosis coughs, speaks, sneezes, spits, laughs or sings.
Although tuberculosis is contagious, it’s not easy to catch. You’re much more likely to get tuberculosis from someone you live or work with than from a stranger. Most people with active TB who’ve had appropriate drug treatment for at least two weeks are no longer contagious.
Treatment
If you have latent TB, your doctor might recommend treatment with medication if you’re at high risk of developing active TB. For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months.
The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
Most common TB drugs
If you have latent tuberculosis, you might need to take only one or two types of TB drugs. Active tuberculosis, particularly if it’s a drug-resistant strain, will require several drugs at once. The most common medications used to treat tuberculosis include:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane)
- Ethambutol (Myambutol)
- Pyrazinamide
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
Some drugs might be added to therapy to counter drug resistance, including:
- Bedaquiline (Sirturo)
- Linezolid (Zyvox)
BEST DR IN ALLAHABAD FOR TUBERCULOSIS
. DR ASHISH SINGH (geogre town, Rama hospital)
. DR VAIBHAV KRISHNA (naini , Rama clinical store)
. DR ABISHEK SINGH(geogre town,Pulmonary care hospital)
. DR SUSHIL KUMAR MISHRA (geogre town, Arogy neuro clinic)
. DR PEEYUSH CHANDRA(M. G marg chandra eye clinic)