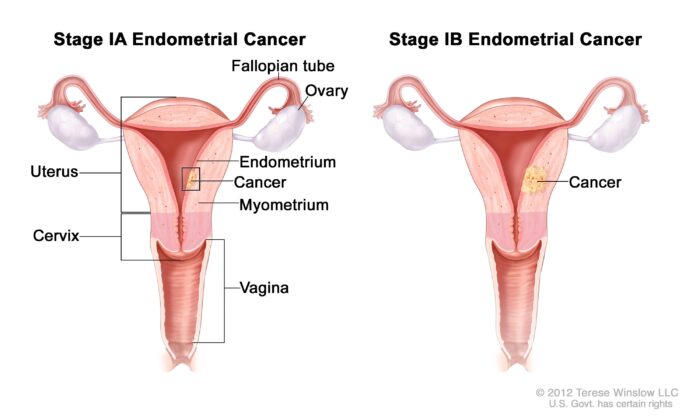
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. It is the most common type of cancer of the uterus and primarily affects postmenopausal women, although it can occur in younger women as well. It is highly treatable if detected early.
Symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding between periods, after menopause, or unusually heavy periods.
- Pelvic pain or pressure.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Changes in bowel or urinary habits.
- Unexplained weight loss.
Causes:
The exact cause of endometrial cancer is not fully understood, but certain factors may increase the risk, including:
- Hormonal imbalances, such as excess estrogen without progesterone.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
- Hormone therapy for breast cancer.
- Family history of endometrial or colorectal cancer.
- Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer).
Treatment:
Treatment for endometrial cancer depends on the stage and individual factors, but may include:
- Surgery: Removal of the uterus and possibly surrounding tissues and lymph nodes (hysterectomy).
- Radiation therapy: High-energy beams to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medications to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy: Medications to block estrogen or progesterone or to lower hormone levels.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that target specific abnormalities in cancer cells.
Prevention:
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent it, some strategies may lower the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor for endometrial cancer.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Use birth control: Oral contraceptives that contain both estrogen and progesterone can help regulate hormone levels.
- Hormone therapy caution: If hormone therapy is necessary, discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider.
- Regular check-ups: Report any abnormal bleeding or other symptoms to a doctor promptly for evaluation.