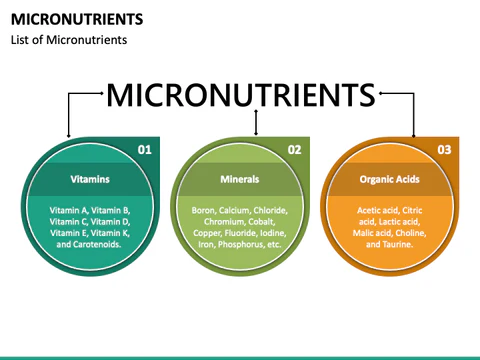
Micronutrients are vital nutrients that the body needs in trace amounts to maintain good health and function. They contain minerals and vitamins that are essential to many physiological functions. An extensive summary of micronutrients is provided below.
vitamins
Organic substances called vitamins are essential for a healthy metabolism. Their solubility separates them into two categories.
Vitamins Soluble in Water:
B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate), and B12 (cobalamin) are the components of the vitamin B complex.
Ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, is essential for collagen formation, the immunological response, and antioxidant defence.
Minerals are inorganic substances that the body requires for a number of processes. Major and trace minerals are the two categories into which they fall:
Principal Minerals:
Calcium is essential for healthy bones, teeth, muscles, and nerve transmission.
Phosphorus is essential for the health of bones and the synthesis of energy.
Energy Production: A number of B vitamins function as coenzymes in metabolic processes that convert proteins, lipids, and carbs into energy.
Antioxidant Defence: Selenium, vitamins C and E, and other nutrients assist in shielding cells from oxidative damage.
Functions of Structure
Bone Health: To keep strong bones and teeth, one needs a diet rich in calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D, and magnesium.
Tissue Growth and Repair: Zinc, vitamin C, and vitamin A all contribute to the development, maintenance, and repair of tissues.
Nutritional Sources
Fruits and vegetables are high in minerals like potassium and magnesium, as well as vitamins like C and folate.
Whole Grains: Supply iron, magnesium, selenium, and B vitamins.