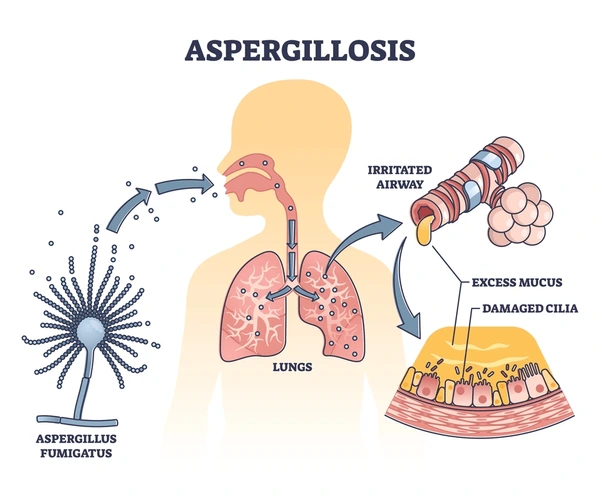
Aspergillosis is an allergic reaction or infection brought on by mold belonging to the Aspergillus species. These fungi are widespread in nature and are present in soil, decomposing plants, and indoor air, especially in places that are wet or have little ventilation. While Aspergillus usually doesn’t harm healthy people, it can seriously harm those who already have lung issues or compromised immune systems.
Symptoms
The kind and intensity of the infection affect the aspergillosis symptoms. Typical symptoms for all kinds consist of:
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Cough (sometimes with blood)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Diagnosis
Aspergillosis diagnosis entails a combination of:
Imaging tests: CT scans or chest X-rays to check for infection symptoms.
Aspergillus can be found through laboratory testing such as tissue biopsies, sputum cultures, and blood tests.
Testing for allergies: Skin or blood testing to look for Aspergillus-related allergic reactions.
Treatment
The kind and degree of aspergillosis determine the course of treatment:
Antifungal drugs: Amphotericin B and voriconazole are two examples of frequently used drugs.
Corticosteroids: Used to lessen inflammation in ABPA.
Surgery: To remove aspergillomas or contaminated tissue, surgery may be required in some circumstances.
It’s critical for people with compromised immune systems or chronic lung diseases to monitor and manage underlying problems.
Avoidance
Reducing exposure to Aspergillus spores is necessary to prevent aspergillosis:
avoiding places where mold or dust are prevalent.
Keeping air purifiers and enough ventilation in houses and offices.
mask wear in areas where mold exposure is possible.
maintaining and cleaning HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems on a regular basis.