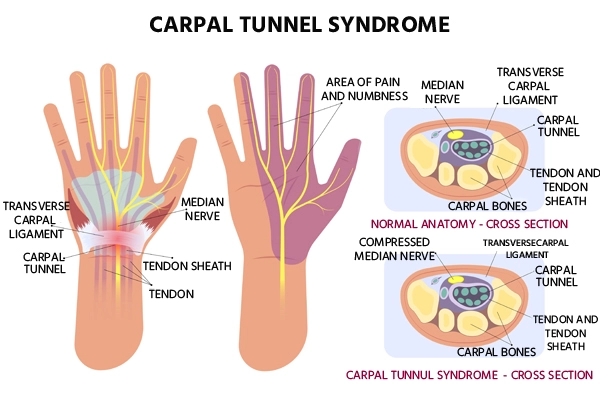
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist.
Overview:
- The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist formed by bones and ligaments.
- The median nerve controls sensations to the palm side of the thumb and fingers (except the little finger), as well as impulses to some small muscles in the hand that allow the fingers and thumb to move.
Symptoms:
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and ring finger.
- Pain or discomfort that may radiate up the arm.
- Weakness in the hand and difficulty gripping objects.
- Sensation of swelling in the fingers without actual swelling being present.
Causes:
- Repetitive motions of the wrist, such as typing or using a mouse for extended periods.
- Prolonged or extreme flexing or extension of the wrist.
- Medical conditions such as diabetes, obesity, or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Trauma or injury to the wrist.
- Certain anatomical factors, such as a smaller carpal tunnel or wrist fractures.
Treatment:
- Rest and immobilization: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and using a splint to keep the wrist in a neutral position can help alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen and stretch the wrist and hand muscles can improve symptoms.
- Corticosteroid injections: Direct injections into the carpal tunnel can provide temporary relief from symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases where other treatments have failed, surgery to relieve pressure on the median nerve may be recommended.
Prevention:
- Take breaks: If your work involves repetitive wrist motions, take frequent breaks to rest your hands and wrists.
- Use proper ergonomics: Maintain good posture and wrist position while working at a computer or performing other repetitive tasks.
- Stretch: Perform stretching exercises for the wrists and hands regularly to help prevent stiffness and improve flexibility.
- Keep a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of developing CTS, so maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent it.