Pthiriasis, also known as “crab lice infestation” or “pubic lice infestation,” is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Pthirus pubis. Here’s an overview of its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms:
- Itching: One of the most common symptoms is intense itching in the affected area, typically the pubic region.
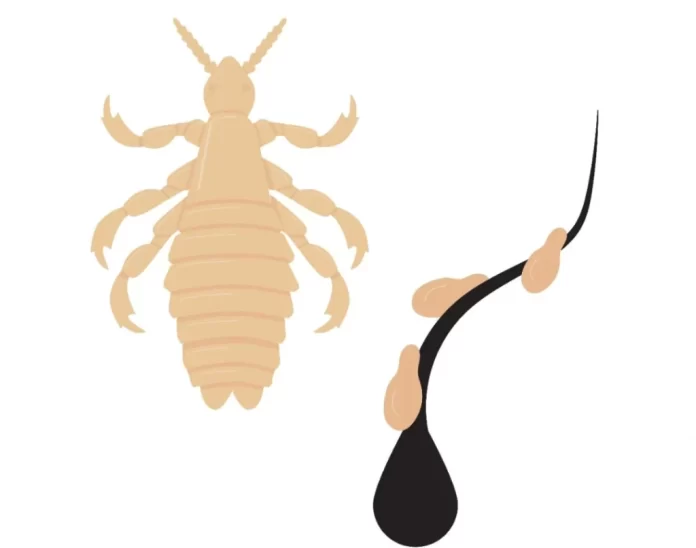
- Visible lice or nits: Tiny, crab-shaped insects or their eggs (nits) may be visible in pubic hair. They can also infest other coarse body hair, such as chest hair, armpit hair, and even eyebrows.
- Red or blue spots: Infestation may cause small, red or blue spots called maculae ceruleae, which are caused by the bites of the lice.
Causes:
Pthiriasis is caused by the infestation of the pubic louse, Pthirus pubis. The infestation usually occurs through close personal contact, most commonly during sexual activity. However, it can also spread through sharing infested clothing, towels, or bedding.
Treatment:
- Medication: Over-the-counter lotions or shampoos containing permethrin or pyrethrin are typically used to kill the lice and their eggs. Prescription medications may be necessary for severe infestations.
- Manual removal: Using a fine-tooth comb to physically remove lice and nits from the affected area can help speed up the treatment process.
- Washing: Washing infested clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water and drying them on high heat can help kill any remaining lice or eggs.
- Avoid scratching: Scratching the affected area can lead to secondary bacterial infections, so it’s important to avoid scratching as much as possible.
Prevention:
- Practice safe sex: Using condoms during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of contracting pubic lice and other sexually transmitted infections.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Avoid sharing clothing, towels, or bedding with individuals who may be infested with pubic lice.
- Regular hygiene: Maintaining good personal hygiene, including regular bathing and washing of clothes and bedding, can help prevent the spread of pubic lice.