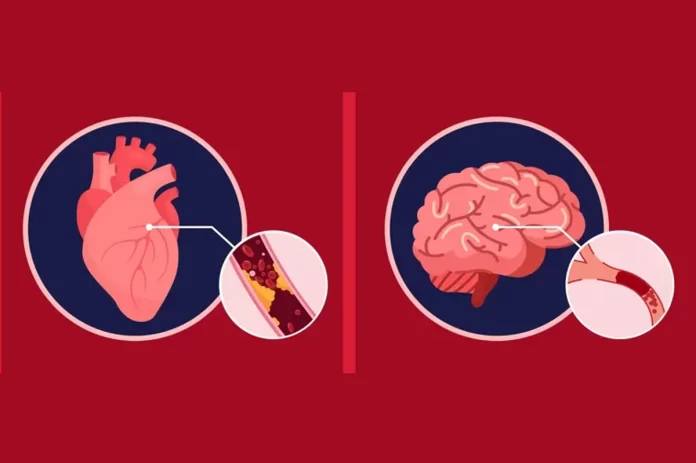
Heart disease and stroke are two of the leading causes of death globally, impacting millions of people each year. Although they are separate conditions, they share some risk factors and prevention strategies.
Heart Disease
Overview
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease (CVD), encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms)
- Valvular heart disease
- Congenital heart defects
Symptoms
Symptoms of heart disease can vary depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Palpitations (irregular heartbeat)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
Causes
Heart disease can be caused by various factors, including:
- Atherosclerosis (buildup of plaque in the arteries)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Family history of heart disease
Treatment
Treatment for heart disease depends on the specific condition and may include:
- Medications: such as statins, blood pressure drugs, and anticoagulants
- Lifestyle changes: diet and exercise modifications, smoking cessation
- Procedures: such as angioplasty or stent placement
- Surgery: such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or valve replacement
Prevention
Preventing heart disease involves managing risk factors, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Following a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Regular physical activity
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
- Controlling blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels
Stroke
Overview
Stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to brain damage.
Symptoms
Symptoms of stroke may include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
- Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause
Causes
The two main types of stroke are:
- Ischemic stroke: caused by a blocked artery (thrombosis or embolism)
- Hemorrhagic stroke: caused by bleeding in the brain due to a ruptured blood vessel
Treatment
Treatment for stroke depends on the type and severity and may include:
- Medications: clot-busting drugs for ischemic stroke or medications to reduce brain pressure for hemorrhagic stroke
- Surgery: to remove blood clots or repair blood vessels in hemorrhagic strokes
- Rehabilitation: physical, occupational, and speech therapy for recovery
Prevention
Preventing stroke involves managing risk factors, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Regular physical activity
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol
In summary, heart disease and stroke are serious conditions that require prompt medical attention and ongoing management. Preventative measures and early intervention can significantly reduce the risk and improve outcomes. Always consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment and prevention plan.