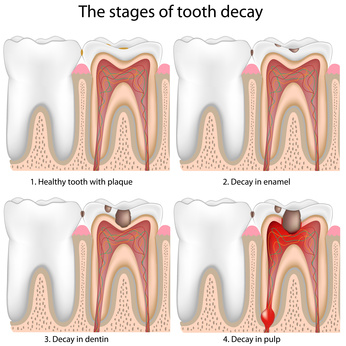
A pocket of pus brought on by a bacterial infection is called a tooth abscess. For various reasons, the abscess may form in different locations close to the tooth. At the tip of the root is where a periapical (per-e-AP-ih-kul) abscess appears. A periodontal abscess, pronounced “per-e-o-DON-tul,” develops in the gingiva next to a tooth root. This page contains information on periapical abscesses.
The most common causes of periapical tooth abscesses are untreated dental cavities, trauma, and previous dental procedures. An abscess at the root tip may result from the infection that follows, which will cause irritation and swelling (inflammation).
A tooth abscess will be drained and the infection removed by dentists. Your tooth might be able to be saved with a root canal procedure. But occasionally, it might be necessary to extract the tooth. Untreated dental abscesses can result in dangerous, potentially fatal consequences.
Signs and Symptoms
Dental abscess symptoms and indicators include:
- severe, ongoing toothache that radiates to your neck, ears, or jaw
- anguish or suffering in both hot and cold climates
- pain or discomfort when biting or chewing is applied.
- high temperature
- facial, cheek, or neck swelling that could make it difficult for you to breathe or swallow
- sore, enlarged lymph nodes in your neck or beneath your jaw
- bad taste in your mouth
- if the abscess bursts, you may experience a sudden rush of salty, foul-tasting, and foul-smelling fluid in your mouth along with pain relief.
Causes
When bacteria infiltrate the dental pulp, a periapical tooth abscess develops. The tooth’s pulp, which is its innermost layer, is home to connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
Bacteria penetrate the tooth through a dental cavity, chip, or crack, and proceed all the way to the root. At the root’s tip, swelling and inflammation may result from the bacterial infection.
Factors at risk
A dental abscess could be more likely if you have these factors:
Inadequate dental hygiene and maintenance. Your risk of dental issues can rise if you don’t take good care of your teeth and gums, which includes not flossing and brushing twice a day. Tooth decay, gum disease, tooth abscess, and other oral and dental issues are possible problems.
A sugar-rich diet. Frequent consumption of sugar-rich foods and beverages, such as sodas and candies, can cause dental cavities and develop into tooth abscesses.
Mouth feeling parched. Tooth decay risk can be elevated by dry mouth. Dry mouth is frequently brought on by side effects from specific medications or aging-related problems.
Complications
An untreated dental abscess will not disappear. In the event of an abscess rupture, you may experience significant pain relief and believe the issue has been resolved; however, you still require dental care.
The infection may spread to your jaw and other parts of your head and neck if the abscess doesn’t drain. An opening between the tooth abscess and the maxillary sinus, which are two large spaces behind your cheekbones and under your eyes, may also develop if the tooth is close to the sinus. An infection in the sinus cavity may result from this. Sepsis, a potentially fatal infection that spreads throughout your body, is another possibility.
An infection that spreads more quickly if you have a compromised immune system and you ignore a tooth abscess.
Prevention
Preventing dental decay is crucial for avoiding dental abscesses. Maintaining good dental hygiene can help prevent tooth decay.
- Fluoridated water should be consumed.
- At least twice a day, brush your teeth for two minutes using fluoride toothpaste.
- Every day, floss between your teeth using dental floss or a water flosser.
- Every three to four months, or whenever the bristles become frayed, replace your toothbrush.
- Consume a balanced diet, avoiding sugar-filled foods and between-meal snacks.
- See your dentist on a regular basis for examinations and cleanings by professionals.
- To provide an additional layer of defence against tooth decay, think about using an antiseptic or a mouthwash containing fluoride.