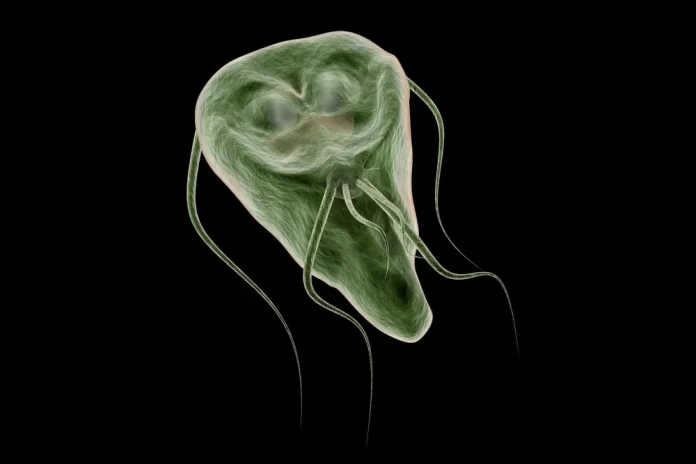
Giardiasis is an infectious disease caused by the parasite Giardia lamblia. It primarily affects the small intestine and is one of the most common causes of waterborne diseases in humans worldwide. Here’s an overview of giardiasis including symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms:
Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Gas or flatulence
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dehydration
Chronic Symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Malaise
- Nutritional deficiencies due to malabsorption
Causes:
Parasite Transmission:
- Giardiasis is primarily transmitted through the ingestion of the Giardia lamblia parasite cysts, which are found in contaminated food or water.
- Direct person-to-person transmission can also occur through the fecal-oral route, especially in crowded or unsanitary conditions.
Risk Factors:
- Drinking untreated water from streams, rivers, or lakes.
- Consuming raw or undercooked food contaminated with Giardia cysts.
- International travel to regions with poor sanitation and hygiene practices.
Treatment:
Medications:
- The primary treatment for giardiasis is antibiotics such as metronidazole, tinidazole, or nitazoxanide. These medications help eliminate the parasite from the body.
- In severe cases or in immunocompromised individuals, a combination of antibiotics may be prescribed.
Symptomatic Relief:
- Over-the-counter medications may be used to alleviate symptoms such as diarrhea and abdominal cramps.
- Rehydration therapy is essential for preventing dehydration, especially in cases of prolonged diarrhea.
Follow-Up Testing:
- After completing the course of antibiotics, follow-up testing may be recommended to ensure the parasite has been fully eliminated from the body.
Prevention:
Water and Food Safety:
- Drink only treated or boiled water, especially when traveling to areas with questionable water sources.
- Avoid consuming untreated water from lakes, rivers, or streams.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consuming, especially if they will be eaten raw.
Good Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating or preparing food, and after using the bathroom.
- Practice good sanitation and hygiene practices, especially in areas with poor sanitation facilities.
Avoidance of High-Risk Activities:
- Avoid swallowing water while swimming in recreational water sources such as lakes, rivers, or pools.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have diarrhea, especially in communal settings.
Proper Disposal of Fecal Matter:
- Ensure proper disposal of feces, especially in outdoor settings such as camping or hiking.
- Use designated latrines or toilets and follow proper waste disposal guidelines.