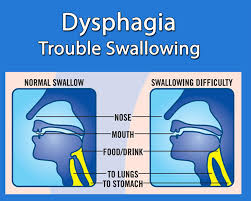
The medical word for trouble swallowing is dysphagia. Dysphagia is sometimes a painful disorder. Certain situations make swallowing impossible.
Occasionally having trouble swallowing—for example, when you eat too quickly or don’t chew your food thoroughly—usually doesn’t mean anything serious. However, persistent dysphagia may be a dangerous illness that requires medical attention.
Although dysphagia can occur at any age, older persons are more likely to experience it. Treatment for swallowing issues is based on the underlying cause, which varies.
 Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms
A few signs of dysphagia are as follows:
- Discomfort when swallowing.
- Being unable of swallowing.
- Having the sensation that food is lodged in one’s chest, throat, or behind the breastbone.
- Drooling in anticipation.
- A harsh voice.
- Food regurgitating, also known as refluxing.
- Frequent heartburn.
- Backflow of food or stomach acid into the throat.
- Reduced weight.
- Gagging or coughing during ingestion.
When to visit a physician
Consult a medical expert if you have weight loss, regurgitation, vomiting, or frequent difficulties swallowing due to dysphagia.
Make an emergency help call right away if breathing becomes difficult due to a blockage. Visit the closest emergency room if you can’t swallow because you feel like food is lodged in your chest or throat.