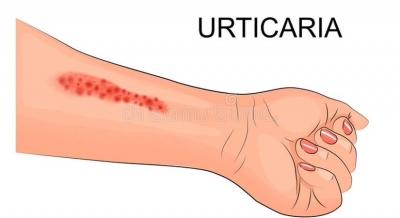
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of red, raised, and itchy welts on the skin. These welts can vary in size and shape and often come and go within a short period. Urticaria is a common condition that can be acute or chronic.
Symptoms:
- Raised, red welts on the skin.
- Itching or a burning sensation.
- Swelling of the affected areas.
- The welts may change shape, move around, and vary in size.
- Sometimes accompanied by angioedema, which involves swelling deeper in the skin, often around the eyes and lips.
Causes:
- Allergic reactions: Common triggers include certain foods, medications, insect stings, or latex.
- Non-allergic factors: Physical triggers such as heat, cold, pressure, or sunlight can cause hives.
- Infections: Some infections may lead to the development of urticaria.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can be associated with chronic urticaria.
- Idiopathic urticaria: In many cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Treatment:
- Antihistamines: These medications help relieve itching and reduce the severity of hives. Non-sedating antihistamines are commonly used for long-term management.
- Corticosteroids: In severe cases, oral or topical corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Epinephrine: In cases of severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis, epinephrine may be administered.
- Avoidance of triggers: Identifying and avoiding specific triggers, when possible, is crucial in managing chronic urticaria.
Prevention:
- Identify and avoid triggers: If specific triggers are known, taking steps to avoid them can help prevent urticaria outbreaks.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can contribute to overall well-being and may help prevent flare-ups.
- Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate urticaria symptoms, so finding stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, may be beneficial.
It’s important for individuals experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of urticaria to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and management. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.