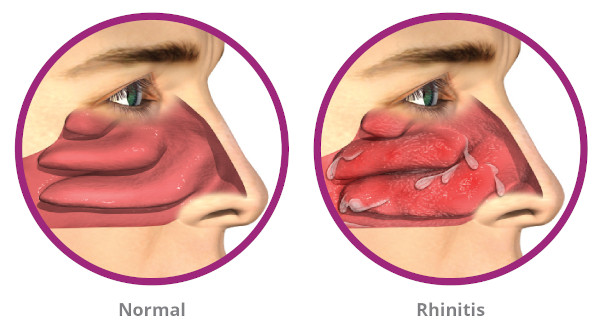
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, is an allergic reaction that occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold. It causes inflammation of the nasal passages, leading to symptoms like sneezing, itching, nasal congestion, and runny nose.
Causes
Allergic rhinitis is caused by exposure to allergens that trigger an immune response in susceptible individuals. Common allergens include pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds, dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and certain foods.
Symptoms
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis can vary in severity and may include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Itchy nose, throat, or eyes
- Watery eyes
- Nasal congestion
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Dark circles under the eyes (allergic shiners)
- Decreased sense of taste or smell
Prevention
Preventing exposure to allergens is key in managing allergic rhinitis. Some preventive measures include:
- Limiting outdoor activities during high pollen seasons
- Keeping windows closed during pollen season and using air conditioning
- Using allergen-proof covers on pillows and mattresses to prevent dust mite exposure
- Regularly cleaning and vacuuming your home to reduce dust and pet dander
- Using a dehumidifier to control indoor humidity and prevent mold growth
- Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke and other air pollutants
Treatment
Treatment for allergic rhinitis aims to alleviate symptoms and may include:
- Antihistamines: These medications block the action of histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions, and can help relieve itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Nasal corticosteroids: These prescription medications reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and can help relieve symptoms like nasal congestion, runny nose, and sneezing.
- Decongestants: These medications can help reduce nasal congestion by shrinking swollen blood vessels in the nasal passages, but they should be used with caution and only for short periods due to the risk of rebound congestion.
- Immunotherapy (allergy shots): In cases of severe allergic rhinitis that do not respond well to other treatments, allergen immunotherapy may be recommended. This involves regular injections of allergens to gradually desensitize the immune system and reduce allergic reactions over time.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis, as they can recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the individual’s symptoms and medical history.