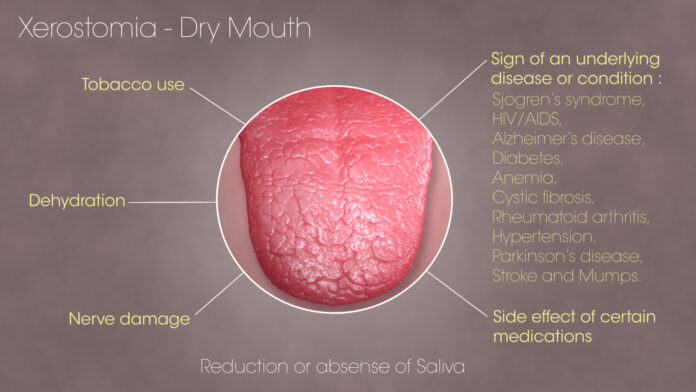
t When your salivary glands are not producing enough saliva to keep your mouth moist, you have a condition known as dry mouth. A common cause of dry mouth is an adverse drug reaction, aging-related conditions, or radiation treatment for cancer. Less frequently, a disorder that affects the salivary glands directly may be the source of dry mouth.
By neutralizing the acids that bacteria make, inhibiting bacterial development, and washing away food particles, saliva helps prevent tooth decay. Additionally, saliva improves flavor perception and facilitates chewing and swallowing. Saliva also contains enzymes that help in digestion.
Reduced saliva production and dry mouth can have a significant impact on your general health, the health of your teeth and gums, as well as your appetite and enjoyment of eating. They can also be merely bothersome.
Symptoms
You may experience all or most of the following indications and symptoms if your saliva production is inadequate:
- Having a dry tongue or a feeling of stickiness
- Saliva that appears to be stringy and thick
- Poor breath
- Chewing, speaking, and swallowing challenges
- Hoarseness, a dry or sore throat, and
- Grainy or dry tongue
- A modified sense of flavor
- Issues with wearing dentures
Causes
When the salivary glands in the mouth are unable to produce enough saliva to keep your mouth moist, dry mouth results. These glands could malfunction as a result of:
Medications. Dry mouth is a common adverse effect of hundreds of treatments, including several over-the-counter medicines. Some of the prescriptions used to treat depression, high blood pressure, and anxiety, as well as some antihistamines, decongestants, muscle relaxants, and painkillers, are among the ones that are more likely to result in issues.
Aging. As they age, many elderly persons have dry mouth. Some drugs, changes in the body’s capacity to handle pharmaceuticals, poor nutrition, and having ongoing health issues are contributing causes.
Cancer treatment. The kind and quantity of saliva produced can change as a result of chemotherapy medications. If the treatment is successful, the normal salivary flow may resume, making this just temporary. Saliva production might significantly decrease as a result of salivary gland damage brought on by radiation treatments to the head and neck. Depending on the radiation dose and the treated location, this could be either transient or permanent.
Nerve harm. It might be brought on by an injury or surgery that damages the nerves in your head and neck region.
Other health issues. Dry mouth may be caused by autoimmune disorders like Sjogren’s syndrome or HIV/AIDS, as well as by ailments like diabetes, stroke, oral yeast infection (thrush), Alzheimer’s disease, or other health conditions. Additionally, breathing and snoring can cause dry mouth.
Alcohol and tobacco usage. Alcohol use, smoking, or tobacco use can all worsen the effects of dry mouth.
Drug use for fun. Methamphetamine usage can result in “meth mouth,” a disease marked by extreme dry mouth and tooth destruction.
Complications
Insufficient saliva can cause, which can result in:
- Gum disease, teeth decay, and more plaque
- Oral sores
- Thrush, a yeast infection of the mouth
- Cracked lips, sores, or split skin around your mouth’s corners
- Nutritional deficiencies brought on by difficulties swallowing and chewing
Treatment
Treatment for relies on a number of variables, including if the patient has an underlying disease or condition and whether they are taking any medications that might be contributing to their dry mouth.
If an underlying reason is identified, certain actions can be taken to lessen its impact.
Medicine: If a certain medicine is suspected of being the source of dry mouth, the doctor will either change the dosage or recommend a different prescription that is less likely to have the same effect.
The medicine pilocarpine (Salagen) or cevimeline (Evoxac), which enhance saliva production, may be prescribed by a physician.
The four main areas of treatment for dry mouth symptoms are as follows:
- Boosting saliva production in order to replace lost secretions
- Preventing dental caries
- Adopting certain actions, including treating infections
An individual with dry mouth should pay extra attention to their oral and dental care. Regular tooth brushing and flossing are crucial. Plaque removal and treatment are additional crucial measures.
- Gum diseases
- Inflammation
- Decay in the teeth