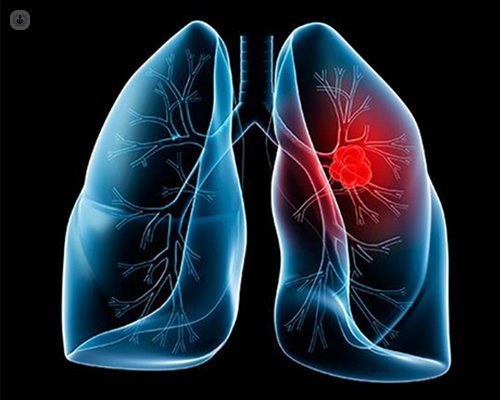
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the lungs, typically in the cells lining the air passages. It is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. In this essay, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of lung cancer.
Causes: The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. Cigarette smoke contains many carcinogens that can damage the DNA in lung cells and lead to cancer. Other factors that increase the risk of lung cancer include exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution. Family history of lung cancer can also increase the risk.
Symptoms: The symptoms of lung cancer can vary depending on the type and stage of the cancer. In the early stages, lung cancer may not cause any symptoms at all. As the cancer progresses, common symptoms may include:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Hoarseness
- Wheezing
- Coughing up blood
Diagnosis: The diagnosis of lung cancer usually involves a combination of imaging tests and tissue samples. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans, can help to identify the presence and location of the cancer. Tissue samples can be taken through various methods, including a biopsy, to confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type of cancer.
Treatment: The treatment of lung cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Surgery is often the first-line treatment for early-stage lung cancer, while chemotherapy and radiation therapy are typically used for more advanced stages. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer treatments that specifically target cancer cells and may be used in combination with other treatments.
In conclusion, lung cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking, but other factors such as exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution can also increase the risk. Symptoms of lung cancer can vary but may include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and weight loss. Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests and tissue samples, and treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of lung cancer or have any risk factors. Early detection and treatment can improve the prognosis for those with lung cancer.