Tripura Floods
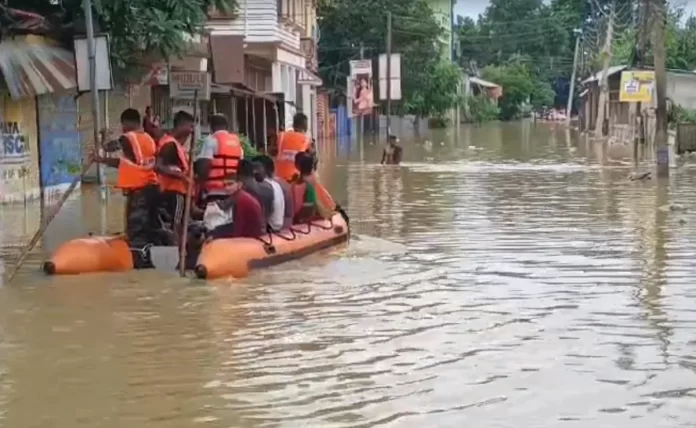
Recent flooding in Tripura, a state in northeastern India, has escalated into a major crisis, with the death toll reaching 22 and over 65,000 people displaced and relocated to emergency shelters. The situation has drawn widespread concern, highlighting the severe impact of natural disasters on vulnerable communities. This article delves into the details of the flood crisis, its implications, and the ongoing response efforts.
1. Severity of the Flooding
Tripura has been grappling with unprecedented flooding due to continuous heavy rainfall exacerbated by the monsoon season. The torrential rains have led to swollen rivers and breached embankments, causing extensive damage to homes, infrastructure, and agricultural land. The severity of the flooding has been compounded by inadequate drainage systems and urban planning issues, which have further hindered effective flood management.
2. Casualties and Displacement
As of the latest reports, the death toll from the floods has tragically reached 22. The floods have caused significant loss of life, including both direct and indirect casualties, such as those resulting from drowning, landslides, and other flood-related incidents. In addition to the fatalities, more than 65,000 individuals have been displaced from their homes. These people have been forced to seek refuge in temporary relief camps set up by the state government and various humanitarian organizations.
3. Relief and Rescue Operations
In response to the crisis, the state government has mobilized resources to provide immediate relief to the affected populations. Relief camps have been established in safer areas, where displaced individuals are provided with essential supplies, including food, clean water, clothing, and medical assistance. The Indian Army, along with local disaster management teams and volunteer organizations, has been actively involved in rescue operations, working to reach those stranded in the flood-affected regions.
4. Infrastructure Damage
The floods have caused significant damage to infrastructure across Tripura. Roads, bridges, and public buildings have been inundated or destroyed, hampering both relief efforts and the daily lives of residents. The transportation network has been severely disrupted, making it challenging to deliver aid to affected areas and complicating evacuation procedures. The destruction of infrastructure also poses a long-term challenge for recovery and reconstruction.
5. Impact on Agriculture
Agriculture, a crucial sector for Tripura’s economy, has been hit hard by the floods. Fields of crops have been submerged, leading to extensive damage to paddy, jute, and other essential crops. This not only affects the immediate food supply but also threatens the livelihoods of many farmers who rely on agriculture as their primary source of income. The economic impact of the floods on agriculture could have long-term repercussions for the state’s food security and economy.
6. Health and Sanitation Concerns
The flooding has raised significant health and sanitation concerns. Stagnant water in the affected areas creates breeding grounds for waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and malaria. The lack of clean drinking water and proper sanitation facilities in relief camps further exacerbates these health risks. Authorities and health organizations are working to provide medical care and improve sanitation conditions to prevent an outbreak of disease.
7. Government and NGO Response
The state government, along with central government agencies, has been coordinating relief efforts to address the immediate needs of the flood-affected population. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and community-based groups have also been playing a crucial role in providing aid and support. The combined efforts of the government and NGOs are vital in managing the crisis, providing emergency relief, and ensuring the well-being of displaced individuals.
8. Challenges in Flood Management
Tripura’s vulnerability to flooding highlights broader challenges in flood management and disaster preparedness. The state’s geographical location and seasonal weather patterns make it prone to such natural disasters. The current crisis underscores the need for improved flood management infrastructure, including better drainage systems, flood barriers, and early warning systems. Investments in these areas could help mitigate the impact of future floods and enhance the state’s resilience to such events.
9. Community and Social Impact
The floods have had a profound social impact on the affected communities. Displacement from homes, loss of personal belongings, and the destruction of community infrastructure have created significant emotional and psychological stress. Community support networks and social services are crucial in providing psychological support and helping individuals cope with the trauma and disruption caused by the floods.
10. Path to Recovery
Recovery from the current flooding will be a lengthy process involving both immediate relief efforts and long-term reconstruction. Rebuilding infrastructure, restoring agricultural production, and ensuring the well-being of displaced individuals will require coordinated efforts from government agencies, NGOs, and local communities. Long-term strategies for flood prevention and disaster management will be essential to reduce the impact of future flooding and build resilience in affected areas.
Conclusion
The floods in Tripura have highlighted the urgent need for effective disaster management and preparedness in vulnerable regions. As the state grapples with the aftermath of the crisis, the combined efforts of the government, NGOs, and the community are crucial in providing relief, addressing immediate needs, and planning for recovery and resilience. The path to recovery will be challenging, but with concerted efforts and strategic planning, Tripura can work towards rebuilding and better preparing for future natural disasters.