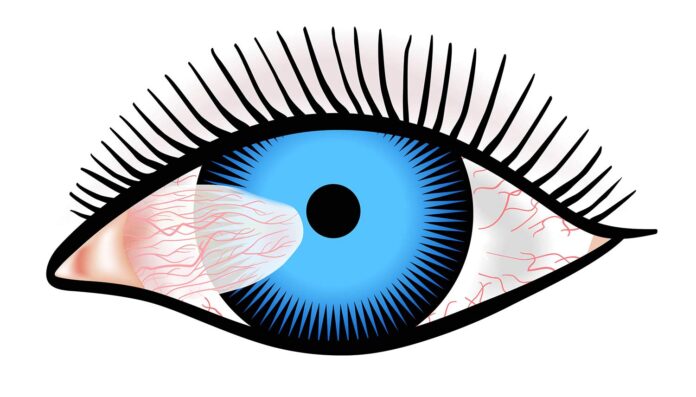
Conjunctival disorders affect the conjunctiva, the thin, transparent tissue covering the white part of the eye (sclera) and the inside of the eyelids. These disorders can result from infections, allergies, environmental irritants, or underlying medical conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms of conjunctival disorders vary depending on the specific condition but commonly include:
- Redness or bloodshot appearance
- Itching or irritation
- Tearing or watery eyes
- Discharge (watery, mucous, or pus-like)
- Swelling of the conjunctiva or eyelids
- Foreign body sensation
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
- Blurred vision
Causes
- Infections:
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Often caused by adenoviruses, highly contagious.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Haemophilus influenzae.
- Chlamydial Conjunctivitis: Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, associated with sexually transmitted infections.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Triggered by allergens such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, or certain medications.
- Irritant Conjunctivitis: Caused by exposure to chemicals, smoke, chlorine, or foreign bodies.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Disorders like Stevens-Johnson syndrome or pemphigoid that affect the conjunctiva.
- Systemic Diseases: Conditions like Kawasaki disease or thyroid eye disease.
Treatment
- Infections:
- Viral: Typically self-limiting; supportive care with artificial tears, cold compresses, and good hygiene.
- Bacterial: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments (e.g., erythromycin, ciprofloxacin).
- Chlamydial: Oral antibiotics (e.g., azithromycin, doxycycline).
- Allergic Conjunctivitis:
- Avoiding known allergens.
- Antihistamine or mast cell stabilizer eye drops (e.g., olopatadine, ketotifen).
- Oral antihistamines.
- Irritant Conjunctivitis:
- Removing the irritant.
- Rinsing eyes with saline solution.
- Lubricant eye drops.
- Autoimmune and Systemic Diseases:
- Managing the underlying condition.
- Topical corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents (under medical supervision).
Prevention
- Hygiene: Regular hand washing, avoiding touching the eyes, and using clean towels and tissues.
- Contact Lens Care: Proper cleaning and storage of contact lenses, avoiding wearing them overnight or while swimming.
- Avoiding Allergens: Identifying and minimizing exposure to known allergens.
- Protective Eyewear: Wearing goggles in environments with chemical exposure or potential eye injury.
- Vaccination: Staying up to date with vaccines to prevent infections that could lead to conjunctival disorders (e.g., measles, rubella).
- Regular Eye Examinations: Early detection and management of potential problems.