Vein disorders occur when veins in the body, primarily in the legs, fail to function properly, leading to improper blood flow. Normally, veins carry blood back to the heart, but when they are damaged, blood can pool, leading to various complications. The most common vein disorders include:
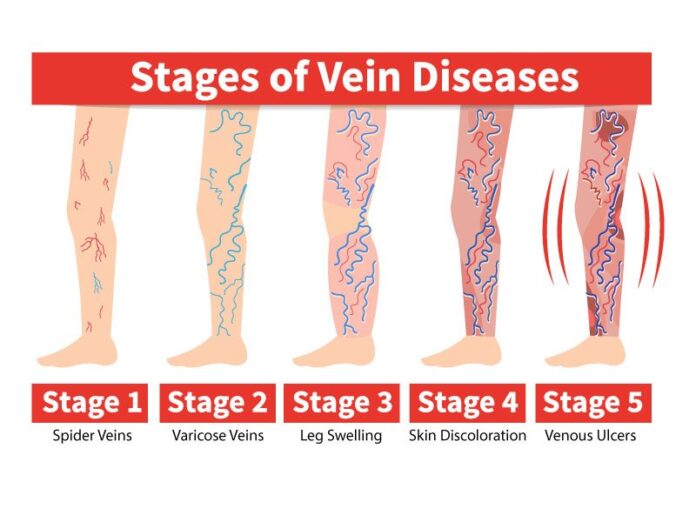
- Varicose Veins: Enlarged, twisted veins often visible under the skin.
- Spider Veins: Smaller, red or purple veins that appear on the surface of the skin.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI): A condition where veins have difficulty sending blood from the legs back to the heart.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot that forms in a deep vein, often in the leg.
Symptoms
Symptoms of vein disorders vary based on the type of condition but commonly include:
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Pain, aching, or a heavy feeling in the legs
- Itching or irritation around veins
- Visible, bulging veins (varicose veins)
- Skin discoloration (brownish or reddish spots)
- Ulcers or sores near the ankles
- Cramps, particularly at night
- Warmth or redness in a leg (indicative of DVT)
Causes
Several factors contribute to vein disorders, including:
- Genetics: Family history of vein issues increases risk.
- Age: The risk increases as veins lose elasticity with age.
- Gender: Women are more prone to vein issues due to hormonal changes.
- Obesity: Extra weight puts additional pressure on veins.
- Prolonged Standing/Sitting: Being in one position for extended periods hinders blood flow.
- Pregnancy: The increased volume of blood during pregnancy can stress veins.
- Injury: Trauma to the legs can damage veins and valves.
Treatment
Treatment for vein disorders depends on the severity and the type of disorder:
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, weight management, elevating legs, avoiding long periods of sitting or standing.
- Compression Stockings: These can improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
- Medications: Blood thinners (for DVT) and pain relievers.
- Sclerotherapy: A procedure where a solution is injected into the veins to collapse them.
- Laser Therapy: Non-invasive treatment using laser energy to seal off affected veins.
- Vein Stripping: Surgical removal of large varicose veins.
- Endovenous Ablation Therapy: Minimally invasive technique using heat to close off damaged veins.
- Catheter-directed Thrombolysis: Used in cases of DVT to dissolve clots.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing vein disorders, consider:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, especially walking, improves circulation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the veins.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Move around or stretch periodically.
- Elevate Legs: Elevating the legs helps blood flow back to the heart.
- Compression Stockings: These can be worn as a preventive measure, particularly for people at higher risk.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Tight clothes around the waist or legs can hinder circulation.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration improves overall blood flow.
Early diagnosis and management can prevent complications from vein disorders, so consult a healthcare provider if symptoms arise.