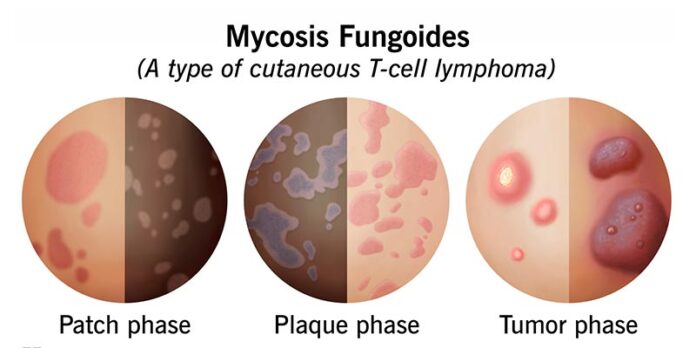
Mycosis fungoides is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that primarily affects the skin. It’s characterized by patches, plaques, or tumors on the skin, which can resemble eczema or psoriasis in the early stages. Here’s an overview of its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms:
- Skin Changes: Patches, plaques, or tumors on the skin, often resembling other skin conditions.
- Itching: Pruritus (itching) is common, sometimes severe.
- Skin Thickening: The affected skin may become thicker or develop a leather-like texture.
- Skin Color Changes: Redness, pigmentation changes, or darkening of the affected skin areas.
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes: Swollen lymph nodes may occur in advanced stages.
Causes:
The exact cause of mycosis fungoides is unknown. It’s thought to be related to T-cells, a type of white blood cell, becoming cancerous and accumulating in the skin. Risk factors may include a weakened immune system and genetic predisposition, but these factors don’t guarantee the development of the disease.
Treatment:
- Skin-directed Therapies: Topical medications like corticosteroids, retinoids, and nitrogen mustard can be applied directly to the skin lesions.
- Phototherapy: Treatment with ultraviolet (UV) light can help reduce skin symptoms.
- Systemic Therapies: For more advanced cases, medications that target cancer cells throughout the body may be prescribed. These include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy X-rays can be used to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Clinical Trials: Patients may also participate in clinical trials for experimental treatments.
Prevention:
Since the exact cause of mycosis fungoides is unknown, there are no specific prevention methods. However, general strategies for maintaining overall health, such as avoiding prolonged exposure to sunlight, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding known carcinogens, may help reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancer, including mycosis fungoides.
Regular skin examinations and prompt medical attention for any unusual skin changes are essential for early detection and treatment of mycosis fungoides. Additionally, individuals with a family history of the disease or other risk factors may benefit from discussing their concerns with a healthcare professional.