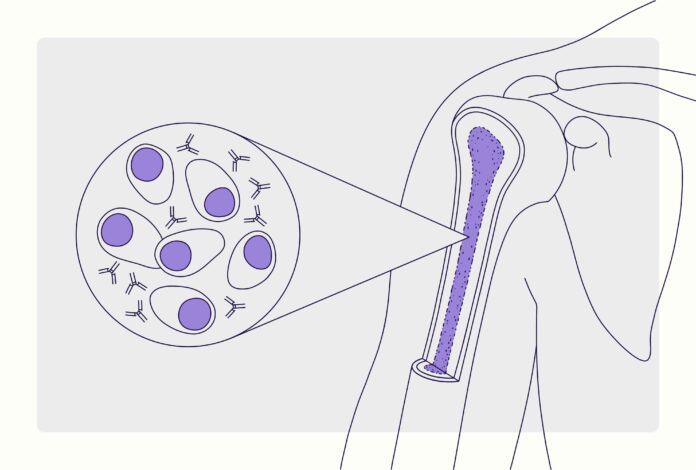
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects plasma cells, a type of white blood cell found in bone marrow. Normally, plasma cells produce antibodies that help fight infections, but in multiple myeloma, abnormal plasma cells (myeloma cells) accumulate in the bone marrow and interfere with the production of normal blood cells. This can lead to weakened bones, impaired immune function, and other complications.
Symptoms:
- Bone Pain: This is one of the most common symptoms, particularly in the back, hips, and skull.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Due to anemia caused by a decrease in red blood cells.
- Frequent Infections: As a result of a weakened immune system.
- Kidney Problems: Myeloma cells can produce proteins that damage the kidneys.
- Hypercalcemia: High levels of calcium in the blood, leading to symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, constipation, nausea, and confusion.
- Nausea, Constipation, Loss of Appetite: These symptoms can occur due to high levels of calcium or kidney problems.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of advanced disease.
Causes:
The exact cause is unknown, but certain factors may increase the risk, including:
- Age: Multiple myeloma is more common in older adults, with the risk increasing with age.
- Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop multiple myeloma than women.
- Race: African Americans are at a higher risk than people of other races.
- Family History: Having a family member with multiple myeloma or other plasma cell disorders may increase the risk.
- Other Plasma Cell Disorders: Conditions like monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) can precede the development of multiple myeloma.
Treatment:
Treatment for multiple myeloma depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease, overall health, and individual preferences. Common treatment options include:
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target abnormalities in cancer cells.
- Immunomodulatory Drugs: Drugs that enhance the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
- Steroids: Medications that can help kill myeloma cells and reduce inflammation.
- Stem Cell Transplant: A procedure to replace diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
Prevention:
There is no guaranteed way to prevent it, but some lifestyle factors may help reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk of multiple myeloma.
- Limit Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as benzene and pesticides, may increase the risk.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help reduce the risk.
- Regular Exercise: Staying physically active can help maintain overall health and reduce the risk of multiple myeloma.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Both smoking and heavy alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of multiple myeloma.