The most prevalent respiratory issue associated with sleep is obstructive sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea patients have frequent respiratory cessations and resumptions during the night.
Sleep apnea comes in several varieties. When the throat muscles relax and obstruct the airway, obstructive sleep apnea develops. During sleep, this frequently occurs on and off. Snoring indicates obstructive sleep apnea.
There are therapies available for obstructive sleep apnea. An apparatus that uses positive pressure to maintain the airway open while you sleep is one kind of treatment. An additional choice is to use a mouthpiece to move the lower jaw forward as you sleep. Surgery may also be a possibility for certain individuals.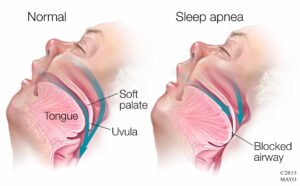
Signs and symptoms
The following are signs of obstructive sleep apnea:
- Excessive drowsiness during the day.
- Loud snoring.
- Instances of breathing stopping while you slept.
- Waking in the middle of the night and choking or gasping.
- Waking up in the morning with a painful throat or dry mouth.
- Headaches in the morning.
- Difficulty focusing in the daytime.
- Alterations in mood, like melancholy or irritability.
- Elevated blood pressure.
When to visit a physician
See a medical professional if any of the following apply to you or your partner:
- Snoring loudly enough to annoy other people or yourself as you sleep.
- Gasping or choking upon awakening.
- Breathing slowly while you’re asleep.
- Becoming excessively sleepy during the day. You might doze off as a result of this while
- Working, watching TV, or even operating a motor vehicle.
Not everyone who snores has obstructive sleep apnea, and snoring does not always mean that there is a major problem.
If you snore loudly, especially if it’s interspersed with stillness, make sure to speak with a member of your healthcare team. Sleeping on your back may result in the loudest snoring and a higher frequency of apneas, or breathing pauses.
Inquire with your medical team about any sleep issue that frequently leaves you feeling drowsy, exhausted, and agitated. Other conditions like narcolepsy may be the cause of excessive daytime sleepiness.




























