Introduction:
Renewable energy sources have become an essential component of the sustainable solution to meet our energy needs in an era of rising environmental consciousness and the urgent need to slow down climate change. It is crucial to switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources as the world’s population and energy needs expand. The goal of this blog is to explore into the realm of renewable energy, underlining its importance, looking at various forms of renewable energy, and talking about how they might help create a sustainable future.
The Right to Education Act (RTE)
Understanding Renewable Energy:
The term “renewable energy” refers to energy sources that regenerate themselves naturally and do no environmental harm. In contrast to fossil fuels, which are limited and increase greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy sources are plentiful and easily accessible. The potential of renewable energy to generate power without consuming natural resources or releasing harmful pollutants is its main benefit.
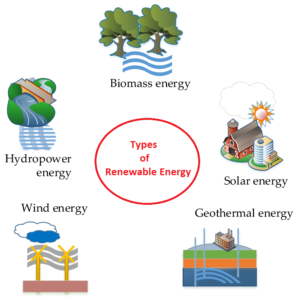
Solar Power:
Solar power is one of the most well-known and often used kind of renewable energy. Solar energy uses the sun’s heat and radiant light to produce power. Photovoltaic (PV) cells found in solar panels turn sunlight into electricity. Solar technology has quickly advanced, becoming more efficient and accessible, and is now widely used in both the household and commercial sectors. The potential for solar energy is enormous, and installation is possible on large tracts of land and rooftops.
Wind Energy:
Utilising the wind’s energy includes turning it into electricity. Wind turbines transform the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity. They are often found in windy areas or offshore. Large-scale wind farms now contribute to the electrical grid, and wind energy has had substantial expansion on a global scale as a mature technology. The effectiveness and performance of wind turbines are being improved by ongoing research and development, making them a more viable and dependable source of renewable energy.
Hydropower:
Electricity is produced by hydropower, which harnesses the force of moving or falling water. Water energy is captured by dams or turbines and transformed first into mechanical energy, then into electrical energy. An important amount of the world’s electricity is produced using hydropower, an established renewable energy source. Because of their negative effects on the environment, large-scale hydropower projects have come under fire, whereas run-of-river and micro-hydropower systems are less harmful to the environment.
Biomass and Bioenergy:
Organic material derived from plants and animals is referred to as biomass. By means of a variety of techniques, including combustion, gasification, and fermentation, biomass can be used to create bioenergy. Biofuels, biogas, and bioelectricity are all types of bioenergy. Utilising agricultural waste, forestry byproducts, and specially bred energy crops are all possibilities with biomass-derived energy sources. However, to maintain its environmental benefits, sustainable management of biomass resources and careful consideration of land usage are essential.
Geothermal Energy:
The heat produced by the Earth’s core is captured through geothermal energy. Utilising subsurface natural heat reserves to produce power or provide heating and cooling for home and commercial use. Geothermal power plants use reservoirs of hot water or steam to turn turbines and generate electricity. Although geothermal energy has enormous potential, its use is only permitted in places where geothermal resources are easily accessible.
Tidal and Wave Energy:
Utilising the strength of ocean tides and waves to produce electricity is known as tidal and wave energy. Wave energy captures the kinetic energy of ocean waves, whereas tidal energy derives from the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. These sources hold a lot of promise for coastal areas even if they are still in the early stages of development. Tidal and wave energy must become more economically viable and effective, which calls for technological advancements and increasing investment.
An energy-based future offers a glimmer of optimism. In addition to lowering greenhouse gas emissions and our reliance on fossil fuels, they also increase our energy security. Using renewable energy sources is crucial as we continue to deal with issues like climate change and environmental deterioration.
Advantages of Renewable Energy:
Environmental Benefits: When compared to fossil fuels, renewable energy sources have a much lower environmental impact. Their greenhouse gas emissions are negligible to nonexistent, lowering their carbon footprint and preventing climate change. Additionally, they improve overall environmental quality by lowering air and water pollution and preserving habitats.
Energy Security: Renewable energy improves energy security by enhancing the diversity of our energy sources. Renewable energy focuses on abundant and locally accessible resources, minimising reliance on imported energy, as opposed to fossil fuels, which are vulnerable to price fluctuation and geopolitical conflicts.
Economic Development and Job Creation: The switch to renewable energy sources offers several chances for both. The market for renewable energy has grown significantly, creating a wide range of employment opportunities in fields ranging from manufacture and installation to research and development.
Sustainable Development: By addressing the triple bottom line of environmental, social, and economic factors, renewable energy is in keeping with the concepts of sustainable development. By decentralising energy production, it encourages inclusive growth, raises living standards, and strengthens local communities.
Overcoming Challenges:
Although renewable energy has great promise, there are some issues that must be resolved:
Storage and Intermittency: Depending on the weather, some renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are intermittent. To increase the dependability and stability of renewable energy systems, efficient energy storage technologies are required to provide a steady supply of electricity during times of low generation.
Infrastructure and grid integration: To integrate renewable energy into current power grids, a reliable transmission infrastructure must be developed. In order to distribute and manage energy from renewable sources efficiently, grid systems must be upgraded to support fluctuating energy inputs.
Cost Competitiveness: Although renewable energy has become more affordable, it still has difficulties competing on price with fossil fuels and requiring a large initial investment. In order to significantly lower prices and make renewable energy commercially feasible, it is imperative to conduct ongoing research, development, and supportive legislation.
Public Acceptance and Awareness: The adoption of renewable energy depends heavily on public acceptance and awareness. Greater community support for renewable energy initiatives and legislation can be attained by educating people about the advantages and clearing up common misconceptions.
Policy Support and Future Outlook:
Through encouraging policies, incentives, and laws, governments all over the world play a crucial role in supporting renewable energy. To hasten the shift, policy frameworks that support investment in renewable energy infrastructure, offer financial incentives, and establish renewable energy targets are essential.
The prospects for renewable energy are encouraging. The rapid adoption of renewable energy sources is being fueled by technological improvements and declining costs. The renewable energy sector is undergoing a transformation because to cutting-edge technologies like floating solar farms, offshore wind parks, and innovative energy storage devices.
Conclusion:
Alternatives to conventional fossil fuels that are environmentally benign and sustainable include renewable energy sources. The world’s energy landscape is changing as a result of solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal, tidal, and wave energy. Their benefits in terms of the impact on the environment, energy security, the generation of jobs, and sustainable development are beyond dispute. The renewable energy revolution will be further accelerated by overcoming obstacles relating to intermittentness, infrastructure, cost competitiveness, and public awareness. We provide the foundation for a greener, more robust, and sustainable future by embracing renewable energy sources.