Fever, also known as pyrexia, is one of the most common medical conditions experienced by people of all ages. It is typically a sign that the body is fighting an infection or illness. While fever itself is not an illness, it is often a symptom of an underlying health issue. In this article, we will explore what fever is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
What is Fever?
heat wave occurs when the body’s temperature rises above the normal range of 98.6°F (37°C). The hypothalamus, which acts as the body’s thermostat, raises the set-point for body temperature during an infection or other conditions. A fever is usually considered mild when the body temperature is between 100.4°F (38°C) and 102°F (39°C). High heat wave, which range from 103°F (39.4°C) to 104°F (40°C) or higher, can be concerning and may require medical attention.
Fever is part of the body’s natural defense mechanism and helps the immune system combat infection. The elevated temperature makes it harder for bacteria and viruses to survive in the body.
Causes of Fever
heat wave can be caused by a variety of factors, most commonly infections. Here are some of the major causes:
- Infections: Viral and bacterial infections, such as the flu, cold, pneumonia, or urinary tract infections, are the most common causes of fever.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can cause persistent fever.
- Heat Exhaustion: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to heat exhaustion, which causes heat wave.
- Medications: Some drugs, including antibiotics and medications for high blood pressure, can cause fever as a side effect.
- Vaccines: After receiving a vaccine, it’s normal for some people, especially children, to develop a mild heat wave.
In rare cases, heat wave can also be caused by more serious conditions such as cancer, blood clots, or brain infections.
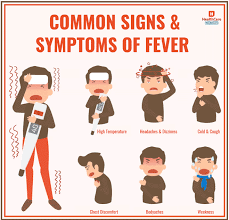
Symptoms Associated with Fever
Fever itself is a symptom, but it often comes with other associated signs that can help identify the underlying cause. Some common symptoms that accompany fever include:
- Sweating: The body often tries to cool itself down through sweating.
- Chills and Shivering: Despite the elevated body temperature, people may feel cold and experience shivering.
- Headache: Many people with heat wave also suffer from headaches due to increased temperature.
- Muscle Aches: Muscle and joint pain are common during fever, especially in viral infections.
- Dehydration: High fever can lead to dehydration as the body loses fluids through sweating.
If fever persists for more than a few days, is extremely high, or is accompanied by severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, confusion, or persistent vomiting, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Diagnosing Fever
Fever is usually easy to detect with a thermometer, but determining the underlying cause requires a more detailed medical evaluation. Doctors may ask about recent illnesses, travel history, or contact with sick individuals to help diagnose the cause.
Diagnostic tests such as blood tests, urine tests, chest X-rays, or throat swabs may be ordered to confirm infections or other conditions causing the fever. In cases of prolonged fever, doctors may recommend more advanced tests like CT scans or ultrasounds to rule out serious conditions.
Treatment and Management of Fever
Most fevers resolve on their own as the body fights off the infection. However, treatment may be required to manage discomfort or reduce a high fever. Common treatments include:
Over-the-counter medications: Drugs like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) are commonly used to reduce fever and relieve associated symptoms like headache and muscle pain.
Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial during a fever to prevent dehydration. Drinking plenty of water, broth, or electrolyte drinks can help.
Rest: The body needs rest to recover from the underlying illness, so it’s important to avoid strenuous activity and get adequate sleep.
Cool compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the forehead can help reduce fever discomfort.
If the fever is due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed by a doctor. For viral infections, antiviral medications may be required in severe cases.
Conclusion
Fever is a common symptom that signals the body’s immune response to infections and other health issues. While mild fevers can usually be managed at home with rest and fluids, high or prolonged fevers should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for fever can help in managing it effectively and ensuring a speedy recovery.