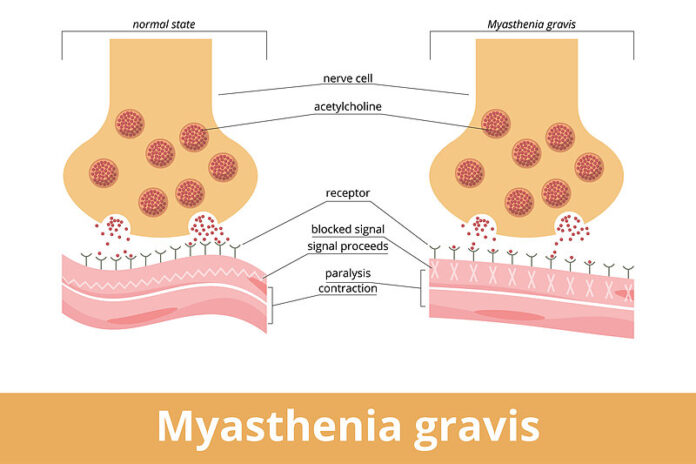
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue, particularly in the muscles that control eye movements, facial expressions, chewing, swallowing, and speaking. Here is an overview of its symptoms, causes, and potential preventive measures:
Symptoms:
- Muscle Weakness: The hallmark symptom of myasthenia gravis is muscle weakness, which tends to worsen with activity and improve with rest. The weakness can affect various muscle groups, including those controlling eye movement, facial expressions, and limb movements.
- Double Vision (Diplopia): Weakness in the muscles that control eye movement can lead to double vision.
- Ptosis: Drooping of the eyelids is another common symptom.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia) and Chewing: Weakness in the muscles involved in swallowing and chewing may lead to difficulties in these activities.
- Fatigue: Muscles tire easily, especially with repetitive movements.
- Speech Difficulties: Weakness in the muscles responsible for speech may result in slurred or nasal speech.
- Shortness of Breath: In severe cases, respiratory muscles may be affected, leading to breathing difficulties.
Causes:
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the neuromuscular junction – the point where nerve signals are transmitted to muscles. This attack is primarily directed at the acetylcholine receptors, disrupting the communication between nerves and muscles.
The exact cause of myasthenia gravis is not well understood, but factors that may contribute include:
- Genetic Factors: There may be a genetic predisposition, as MG sometimes occurs in families.
- Thymus Gland Abnormalities: The thymus gland, which plays a role in the immune system, is often abnormal in people with MG.
- Other Autoimmune Disorders: MG may be associated with other autoimmune conditions.
Prevention:
While there is no known way to prevent myasthenia gravis, certain measures may help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Medical Treatment: Medications such as cholinesterase inhibitors and immunosuppressants are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms and suppress the immune system’s attack on the neuromuscular junction.
- Thymectomy: Surgical removal of the thymus gland is sometimes recommended, especially in cases where the gland is abnormal.
- Lifestyle Management: Conserving energy, avoiding stress, and getting adequate rest can help manage fatigue and muscle weakness.
- Regular Follow-up: Regular medical check-ups and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor and adjust treatment as needed.
It’s important for individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of myasthenia gravis to seek prompt medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Treatment and management strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.