Saliva can transmit the infectious mononucleosis, often known as glandular fever. Fever, sore throat, exhaustion, and enlarged lymph nodes are among the symptoms.
The most common cause of glandular fever is an infection with the extremely contagious Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a herpes virus.
According to experts, the prevalence of EBV infections among persons globally is estimated to be over 90%. It does not, however, necessarily result in glandular fever or symptoms. Similar symptoms can be seen in cases of parasite toxoplasmosis as well as glandular fever caused by cytomegalovirus infection and rubella, sometimes known as German measles.
Although glandular fever typically goes away on its own, there is no known cure. The weariness, though, may not go away quickly.
Symptoms
The symptoms of glandular fever often manifest 4-6 weeks following the initial infection (Trusted Source).
A person could encounter:
- Symptoms similar to the flu, such as headaches and body aches
- A minimum temperature of 100.4°F (38°C).
- An extensive, non-itching rash
- Sickness as well as appetite loss
- Weakness, weariness, lethargy, and malaise
- Puffiness and edoema surrounding the eyes
- A painful throat
- Enlargement of the lymph glands
- Upper abdominal pain brought on by a large spleen
- Liver aches and yellowing
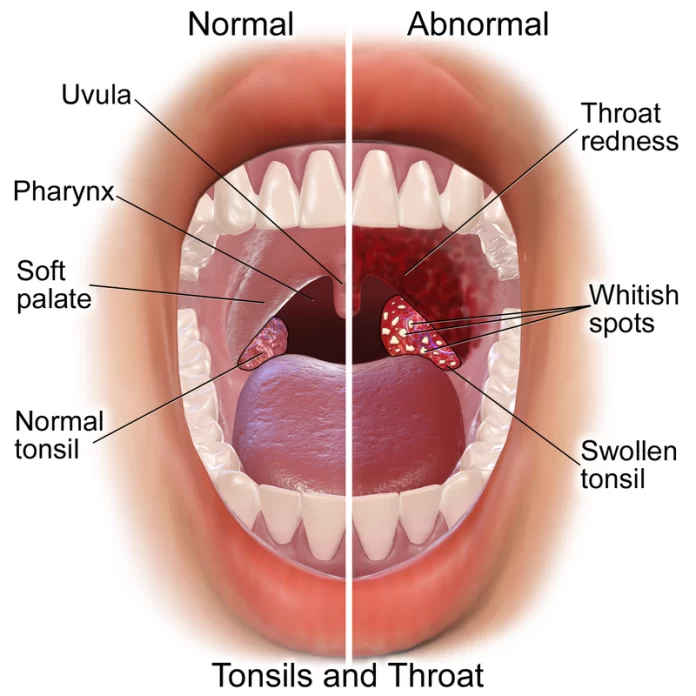
The throat
Though it can be moderate at times, the soreness is frequently intense and accompanied by swelling and redness, much like tonsilitis. Painful swallowing is common.
Should the symptoms of what appears to be acute tonsillitis persist longer than usual, glandular fever may be the cause.
The spleen and lymph nodes
The lymph nodes enlarge as the immune system battles the infection. Any lymph node may enlarge, but the neck and armpit nodes typically have the most noticeable swelling. They might be delicate.
Located on the left side of the abdomen beneath the ribs, the spleen is a component of the immune system.
As the body fights the illness, the spleen may also swell; the affected person may feel it growing beneath their ribcage. The upper left region of the abdomen may experience minor pain due to the swelling.
The hepatic
Hepatitis, a minor inflammation of the liver, is a rare side effect of EBV. Rarely, it may also result in abrupt liver failure. People over 40 are more likely to experience thisTrusted Source.
Hepatitis symptoms include:
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes, or jaundice
- Aversion to alcohol
- A decrease in appetite
- Sick stomach
- Hepatitis and jaundice ought to go away as the glandular fever patient heals.
Reasons
The majority of EBV infections happen in early childhood. In order to combat the virus, the immune system creates antibodies when it occurs.
The virus stays dormant in the blood cells and the pharynx for the duration of one’s life. Lifelong immunity is provided by the antibodies, and glandular fever seldom recurs.
Occasionally, though, the pathogen reactivates Trusted Source. Occasionally, this may result in symptoms, particularly in those with compromised immune systems. Nevertheless, glandular fever or other symptoms are not necessarily the result of an EBV infection.
A person is more likely to experience glandular fever if they get the virus when they are a teenager or young adult. It mostly affects persons between the ages of 15 and 24.Reliable Source
Glandsular fever affects at least 1 in 4Trusted Source young adults infected with EBV. People in other age groups are less frequently impacted by the sickness.
Treatment
Though exhaustion may persist longer, most people find that their symptoms disappear in 2-4 weeks even in the absence of treatmentTrusted Source.
To aid in the body’s healing process, a person can do the following:
Relax
While glandular fever patients frequently feel too fatigued and sick to carry out their regular activities, total rest is essential, particularly in the first month following the onset of symptoms.
Light exercise may aid in the person’s recovery and help them rebuild their muscle strength.
Consume lots of liquids.
This will assist in avoiding dehydration, particularly in the event of a fever.
It can be difficult to swallow when you have a sore throat, but it’s crucial to drink enough water.
Medication for pain alleviation
Over-the-counter and online sources offer pain relievers such acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil). They might lessen the symptoms of fever.
Scoffing
Gargling with a pharmaceutical solution or salt water can help soothe a sore throat.
Androgens
Should the infection result in tonsil inflammation, a physician can recommend a brief course of corticosteroids.