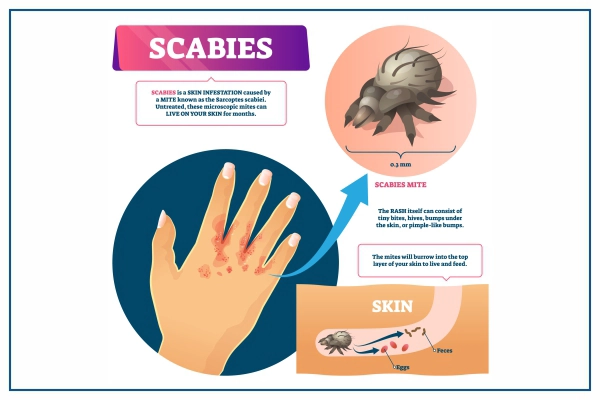
Sarcoptes scabiei, a microscopic burrowing mite, is the source of the irritating skin rash known as scabies. In the place where the mite burrows, there is intense itching. At night, the urge to scratch could be more intense.
In a household, child care facility, classroom, nursing home, or prison, close person-to-person contact can spread scabies quickly. Since scabies spreads so easily, medical professionals frequently advise treating every member of the household as well as any close contacts.
Treating it is simple. The scabies-causing mites and their eggs are eliminated by medicated skin lotions and pills. However, weeks may pass before the itching stops despite medication.
Ailments
Symptoms include:
- Itching that is typically acute and worse at night
- Thin, wavy skin tunnels composed of small blisters or lumps
Skin creases are frequently the site of scabies. However, it can develop on a variety of bodily areas. It is most commonly found in adults and older children:
- In between the toes and fingers
- Under the arms
- Around the midsection
- Along the wrists’ interiors
- Within the elbows
- The bottoms of the shoes
- Across the chest
- Concerning the nipples
- Around the button in the belly
- Close to the genitalia
- Around the groyne
- On the rear end
The following are typical locations for scabies in newborns and early children:
- Digits
- Neck, face, and scalp
- Fingers of the palms
- The foot soles
If you’ve already had scabies, symptoms could appear a few days after exposure. The onset of symptoms may take up to six weeks if you have never had scabies. Even in the absence of symptoms, scabies can still spread.
When to visit a physician
If you have any scabies symptoms, consult your physician.
Numerous skin diseases, like dermatitis and eczema, can also result in skin lumps and itching. In order to give you with the appropriate care, your healthcare professional can identify the precise origin of your symptoms. Lotions without a prescription or antihistamines can help reduce irritation. However, neither the mites nor their eggs will go away.
Reasons
A tiny, eight-legged mite is responsible for scabies. The female mite excavates a tunnel beneath the skin in which to lay her eggs.
After the eggs hatch, the mite larvae move to the skin’s surface to develop. After then, these mites may move to other skin regions or to other people’s skin. The body’s allergic response to the mites, their eggs, and their excrement results in itching.
The mites can spread through close skin-to-skin contact and, less frequently, through sharing clothing or bedding with a person who has scabies.
Humans do not contract scabies from pets. In humans, the scabies mites that infect animals do not live or proliferate.
However, if the mite goes under the skin, coming into contact with an animal that has scabies may cause momentary itching. But the mite will expire in a few days. Thus, no treatment is required.
Avoidance
Take these actions to stop the mites from spreading to other persons and to stop it from returning:
Clean all garments and bedding. The mites and their eggs are killed by heat. Before starting treatment, wash any garments, towels, and bedding in hot, soapy water that have been used in the previous three days. Using a high heat, dry. Anything you can’t wash at home, dry clean it.
Let the mites starve. Stow anything that aren’t washable in airtight plastic bags and store them somewhere out of the way, like your garage, for a week. Without nourishment, mites perish in a matter of days.
Vacuum and clean. Cleaning your house is an excellent idea if you want to stop scabies from spreading. This is especially valid for scabies patients who have crusted. To get rid of scales and crusts that could contain scabies mites, hoover floors, carpets and furniture.