Headache disorders, characterized by recurrent headache, are among the most common disorders of the nervous system.
Important information
1-One of the most prevalent illnesses of the nervous system is headache.
2-Nearly half of adults, according to estimates, experienced a headache at least once in the previous 12 months.
3-Recurrent headaches are the hallmark of headache disorders, which have a negative impact on quality of life, disability, and financial resources for both individuals and society.
4-Only a small percentage of persons with headache issues are correctly diagnosed by a medical professional worldwide.
5-All around the world, headache is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and underappreciated.
How prevalent are headache conditions?
According to estimates, 50% of adults worldwide have a current headache condition (symptomatic at least once in the last year). In the past year, 50% to 75% of adults in the world between the ages of 18 and 65 have experienced headaches; of them, 30% or more have reported migraine. 1.7–4% of adults worldwide experience headaches 15 or more days a month. Despite regional differences, headache disorders are a global issue that affect people from various ages, races, socioeconomic backgrounds, and geographical locations.
What are the costs associated with headache disorders?
Headaches are not only uncomfortable, but also incapacitating. Migraine was identified as the sixth most common cause of years lost due to disability (YLD) globally in the Global Burden of Disease Study, which was updated in 2013. The prevalence of headache disorders as a whole was third.
Headache disorders impose a recognizable burden on sufferers including sometimes substantial personal suffering, impaired quality of life and financial cost. Repeated headache attacks, and often the constant fear of the next one, damage family life, social life and employment. The long-term effort of coping with a chronic headache disorder may also predispose the individual to other illnesses. For example, anxiety and depression are significantly more common in people with migraine than in healthy individuals.
Types of headache conditions
Since they cause a significant portion of the population’s impairment and ill-health, migraine, tension-type headache, and medication-overuse headache are important for public health.
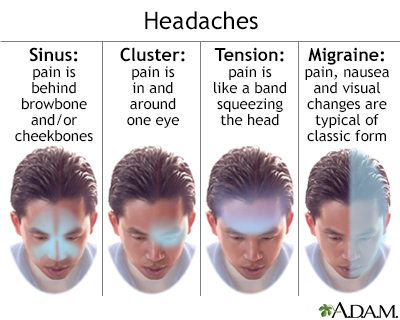
Migraine
- A primary headache disorder.
- Migraine most often begins at puberty and most affects those aged between 35 and 45 years.
- It is more common in women, usually by a factor of about 2:1, because of hormonal influences.
- It is caused by the activation of a mechanism deep in the brain that leads to release of pain-producing inflammatory substances around the nerves and blood vessels of the head.
- Migraine is recurrent, often life-long, and characterized by recurring attacks.
- Attacks typically include:
- headache, which is:
- of moderate or severe intensity
- one-sided
- pulsating in quality
- aggravated by routine physical activity
- with duration of hours to 2-3 days
- nausea (the most characteristic associated feature);
- attack frequency is anywhere between once a year and once a week; and
- in children, attacks tend to be of shorter duration and abdominal symptoms more prominent.
- headache, which is:
Tension-type headache (TTH)
-
-
- TTH is the most common primary headache disorder.
- Episodic TTH, occurring on fewer than 15 days per month, is reported by more than 70% of some populations.
- Chronic TTH, occurring on more than 15 days per month, affects 1-3% of adults.
- TTH often begins during the teenage years, affecting three women to every two men.
- Its mechanism may be stress-related or associated with musculoskeletal problems in the neck.
- Episodic TTH attacks usually last a few hours, but can persist for several days.
- Chronic TTH can be unremitting and is much more disabling than episodic TTH.
- This headache is described as pressure or tightness, often like a band around the head, sometimes spreading into or from the neck.
-
Cluster Headache (CH)
- A primary headache disorder.
- CH is relatively uncommon affecting fewer than 1 in 1000 adults, affecting six men to each woman.
- Most people developing CH are in their 20s or older.
- It is characterized by frequently recurring (up to several times a day), brief but extremely severe headache, usually focused in or around one eye, with tearing and redness of the eye, the nose runs or is blocked on the affected side and the eyelid may droop.
- CH has episodic and chronic forms.
Medication-overuse headache (MOH)
-
-
-
- MOH is caused by chronic and excessive use of medication to treat headache.
- MOH is the most common secondary headache disorder.
- It may affect up to 5% of some populations, women more than men.
- MOH occurs by definition on more days than not, is oppressive, persistent and often at its worst on awakening.
-
-
The financial and social cost of headache
Given the related impairment and monetary costs to society, headache disorders are a public health concern. Estimates of the financial cost of headache disorders to society are enormous, primarily due to lost working hours and decreased output, as they are most problematic during the productive years (late teens to 50s). Approximately 25 million working or school days are lost annually in the United Kingdom due to migraine alone; the combined costs of TTH and MOH may equal this financial burden. One analysis found that one-third of all neurological consultations were for headache, making headache a common reason for seeing a doctor.
However, many people who suffer from headaches do not obtain good care. For instance, only half of those who were diagnosed with migraine in the United States and the United Kingdom had visited a doctor during the preceding 12 months for headache-related reasons, and only two-thirds had the condition correctly diagnosed. The majority just used over-the-counter drugs.
Treatment
Training of healthcare professionals, accurate diagnosis and recognition of the diseases, suitable therapy with affordable drugs, easy lifestyle changes, and patient education are all necessary for the appropriate treatment of headache disorders. Analgesics, anti-emetics, certain anti-migraine medications, and preventive medications are the primary kinds of medications used to treat headache disorders.
WHO reaction
This clear weight necessitates action. WHO acknowledges this and collaborates on the global campaign against headaches with the non-governmental organization Lifting The Burden. This global movement, which started in 2004, aims to improve both the quality and accessibility of headache care while also increasing awareness of headache diseases. The Atlas of Headache diseases, published in 2011 by WHO, details the burden caused by headache diseases and the resources available to lessen it.