Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21. This condition affects approximately 1 in every 700 births worldwide. It is named after John Langdon Down, a physician who first described the syndrome in 1866.
Causes: Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the cells of the body. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristic features of Down syndrome.
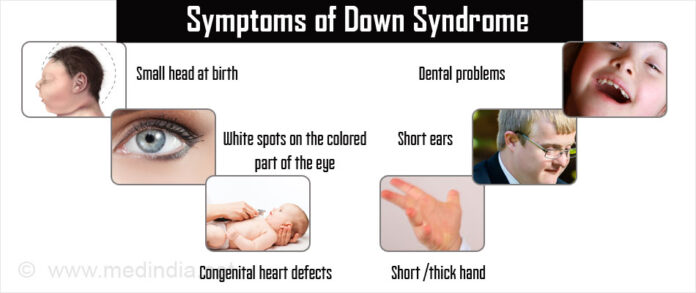
Symptoms: People with it may have physical and intellectual disabilities, and they may also be at increased risk for certain health conditions. Some common physical features of Down syndrome include:
- Flat facial features
- Small head and ears
- Short neck
- Poor muscle tone
- Small hands and feet
- Upward slanting eyes, with small skin folds at the inner corners
- A single deep crease across the center of the palm
- Hyperflexibility (excessive joint movement)
Intellectual disabilities can range from mild to severe, and individuals with this syndrome may also have delayed speech and language development, and may be slower to reach developmental milestones.
Diagnosis: Down syndrome can be diagnosed during pregnancy through various screening tests, such as ultrasound and maternal blood tests. If these tests indicate a higher risk for Down syndrome, further diagnostic testing, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, can be done to confirm the diagnosis. After birth, a physical examination and genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of it.
Treatment: There is no cure for it, but early intervention and treatment can improve the overall quality of life for individuals with the condition. Treatment may include:
- Early childhood intervention programs, including speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy
- Special education services
- Medical treatment for any associated health conditions, such as heart defects or hearing loss
- Behavioral and mental health counseling for individuals and families
In summary, it is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21. Individuals with Down syndrome may have physical and intellectual disabilities, and may be at increased risk for certain health conditions. Early intervention and treatment can improve outcomes for individuals with Down syndrome.