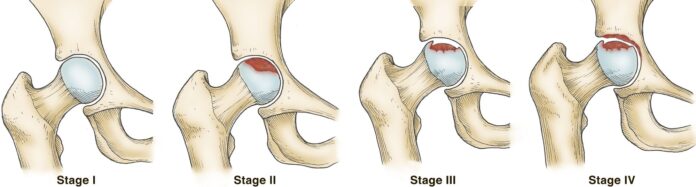
Osteonecrosis, also known as avascular necrosis, is a condition where there is a loss of blood flow to a bone, leading to its death. Here’s an overview of its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
- Symptoms:
- Initially, there might be no symptoms.
- As the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
- Pain in the affected joint (commonly the hip, knee, shoulder, or ankle).
- Limited range of motion.
- Stiffness.
- Joint instability.
- Difficulty in weight-bearing.
- Causes:
- Osteonecrosis can be caused by various factors disrupting blood flow to the bone. Common causes include:
- Trauma or injury to the bone.
- Chronic use of corticosteroids.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Certain medical conditions like sickle cell disease, lupus, and HIV/AIDS.
- Joint surgery or other medical procedures that may affect blood flow to the bone.
- Radiation therapy.
- Osteonecrosis can be caused by various factors disrupting blood flow to the bone. Common causes include:
- Treatment:
- Treatment aims to relieve pain, improve joint function, and prevent further damage to the bone. Options include:
- Medications to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy to improve joint function and strengthen surrounding muscles.
- Using assistive devices like crutches or braces to reduce stress on the affected joint.
- Core decompression: Removing part of the inner layer of the bone to relieve pressure and increase blood flow.
- Osteotomy: Surgical reshaping of the bone to reduce stress on the affected area.
- Joint replacement surgery in severe cases where the joint is severely damaged.
- Treatment aims to relieve pain, improve joint function, and prevent further damage to the bone. Options include:
- Prevention:
- While some risk factors for osteonecrosis, like trauma or certain medical conditions, may not be preventable, there are steps individuals can take to lower their risk:
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Avoid excessive use of corticosteroids, or use them under medical supervision.
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly.
- Manage underlying medical conditions effectively.
- Avoid smoking, as it can restrict blood flow to the bones and tissues.
- Follow proper safety precautions during joint surgery or other medical procedures.
- While some risk factors for osteonecrosis, like trauma or certain medical conditions, may not be preventable, there are steps individuals can take to lower their risk: