Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which are nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. This condition can cause various symptoms depending on the type and location of the affected nerves. Here’s an overview of peripheral neuropathy, including symptoms, causes, and prevention:
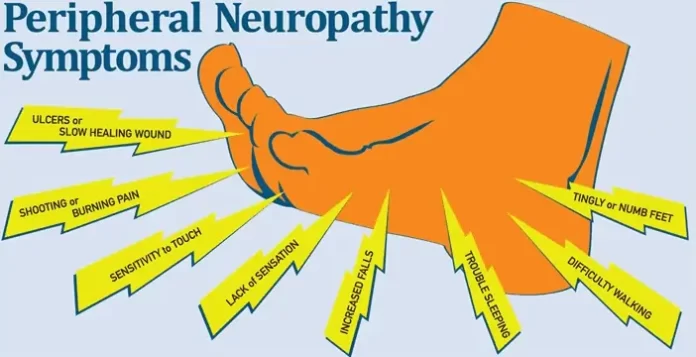
Symptoms:
- Numbness, tingling, or prickling sensations in the hands or feet (often starting in the toes or fingers and spreading upward)
- Sharp, burning, or shooting pain
- Muscle weakness or difficulty moving the affected body part
- Sensitivity to touch
- Loss of coordination and balance
- Changes in blood pressure or heart rate
- Digestive issues like constipation, diarrhea, or difficulty swallowing
Causes:
Diabetes: The most common cause of peripheral neuropathy, affecting nerves due to prolonged high blood sugar levels.
Trauma or injury: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can damage peripheral nerves.
Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can lead to nerve damage.
Infections: Viral or bacterial infections such as HIV, Lyme disease, and shingles can cause neuropathy.
Hereditary disorders: Genetic conditions like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease can result in peripheral neuropathy.
Alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to nerve damage.
Medications: Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, can cause peripheral neuropathy as a side effect.
Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients like vitamins B1, B6, B12, and E can contribute to nerve damage.
Prevention:
Manage underlying conditions: Control blood sugar levels if you have diabetes, and seek treatment for autoimmune diseases or infections promptly.
Protect against injury: Take precautions to avoid accidents and minimize the risk of trauma.
Limit alcohol consumption: Drink alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether to prevent alcohol-related neuropathy.
Maintain a balanced diet: Ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals through a healthy diet or supplements as needed.
Exercise regularly: Engage in physical activity to improve circulation and overall nerve health.
Avoid toxic substances: Limit exposure to toxins, including certain medications and environmental pollutants.
While some causes of peripheral neuropathy may not be preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions can help reduce the risk or slow the progression of nerve damage. If you experience symptoms of peripheral neuropathy, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.