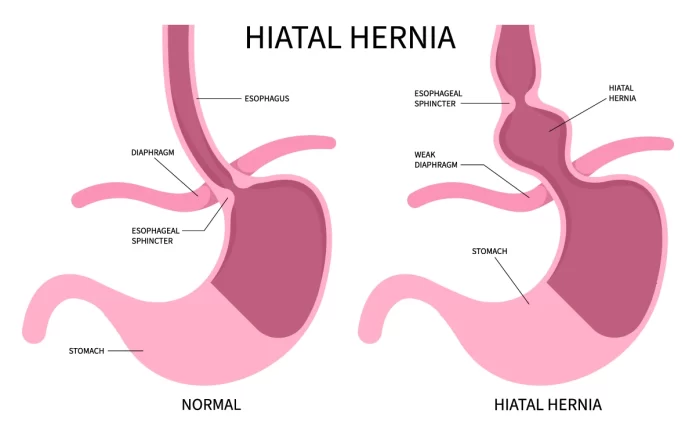
Hiatus hernia, also known as hiatal hernia, is a condition where a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Below is an overview of hiatus hernia covering its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating.
- Regurgitation: Bringing food back up into the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing: Feeling like food is stuck in the throat.
- Chest pain: May resemble symptoms of a heart attack.
- Belching or hiccups: Excessive burping or hiccuping.
Causes:
- Weakness in the diaphragm: The hiatus (an opening in the diaphragm) weakens, allowing the stomach to protrude upward.
- Increased pressure on the abdomen: Factors such as obesity, pregnancy, heavy lifting, or straining during bowel movements can increase abdominal pressure and contribute to hiatus hernia development.
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes: Dietary modifications, such as avoiding large meals, acidic or spicy foods, and alcohol, can help reduce symptoms. Weight loss and avoiding tight clothing can also alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Over-the-counter antacids, H2 receptor blockers, or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help alleviate symptoms by reducing stomach acid production.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when lifestyle and medication management are ineffective, surgical repair of the hernia may be necessary to reposition the stomach and strengthen the hiatus.
Prevention:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases the risk of hiatus hernia, so maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help prevent its development.
- Avoid triggering foods: Certain foods and beverages, such as fatty foods, citrus fruits, caffeine, and alcohol, can exacerbate symptoms, so avoiding them may help prevent discomfort.
- Practice good posture: Poor posture can increase pressure on the abdomen and contribute to hernia development, so maintaining good posture while sitting and standing can help reduce the risk.
In conclusion, hiatus hernia is a condition characterized by the protrusion of the stomach through the diaphragm, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. It is primarily caused by weaknesses in the diaphragm or increased abdominal pressure. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery, depending on the severity of symptoms, while prevention focuses on maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding triggers that exacerbate symptoms.