A bruise in your muscle is called a muscle contusion. Your muscle fibres and connective tissue are crushed when a blunt item strikes you directly and doesn’t split your skin, resulting in an excruciating injury. This causes your muscle’s supporting blood vessels to burst, which causes bleeding into the injured muscle.
Muscle bruises are invisible, in contrast to skin bruises. However, the majority of muscle contusions hurt, so you can feel it.
There are various severity levels for muscle contusions. The majority of contusions recover with at-home care.
Symptoms and Causes
What signs of a contusion in the muscle are present?
Painful muscle contusions are the norm. The following symptoms could be present in you, depending on the extent of the injury:
- Edoema, or swelling, in the afflicted area.
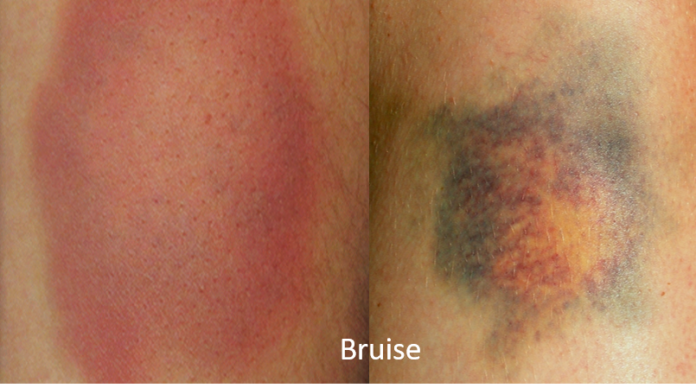
- Bruises on skin.
- Rigidity or weakness in the damaged muscle.
- Having trouble using the joint or joints that are injured.
Depending on how severe the damage was, you can also suffer more injuries, such as:
- A hematoma in your muscles is a collection of blood.
- A sprain is when a ligament in a joint tears or stretches.
- Joint dislocation.
- Tense muscles.
- Fractured limb.
- Harm to your internal organs in the event that your abdomen was struck.
Why do muscles contusion occurs?
A muscle contusion (bruise) is typically caused by a direct, blunt blow to one of your muscles. Athletes frequently experience this when playing contact or intense sports. However, a contusion could result from any direct hit, such as colliding with or falling upon a blunt item.
For instance, one of the most typical injuries in contact sports, particularly American football, is a contusion of the quadriceps (thigh muscles). Since your thigh muscles are among the biggest in your body, they are frequently targeted. These muscles are susceptible to bruises from hard impacts such as tackling or falling on top of someone.
What consequences could a contusioned muscle cause?
The following are potential side effects of moderate to severe muscular contusions:
Compression inside and around your muscle might cause compartment syndrome. Pressure might result from fast bleeding in a contusion of the muscle. This syndrome can be deadly and is quite painful. The supply of blood, oxygen, and nutrients to muscles and neurons can be restricted by compartment syndrome. It may necessitate immediate surgery and cause catastrophic damage. Visit the hospital right once if you have weakness and numbness in the wounded area, as well as fast growing swelling.
Myositis ossificans: This is the result of traumatic injury-induced bone formation within the muscle. If you attempt to rehab the muscle too soon after a serious contusion, it might occasionally develop. Two to four weeks following the accident may pass before myositis ossificans becomes apparent.
Prevention
Similar to how not all injuries may be avoided, not all contusions of the muscles can be avoided. However, you can take the following actions to reduce your chance of developing a muscle contusion:
- To avoid overusing your muscles, adequately train and exercise.
- Exercises should be done both before and after sports.
- When participating in extreme sports or other contact activities, wear protection gear.
- To avoid falls, make sure your living area is free of debris and other trip risks.
- Use a walking aid, such as a cane or walker, if your risk of falling is higher.
- You should think about avoiding activities that can cause injuries if you have a bleeding issue.