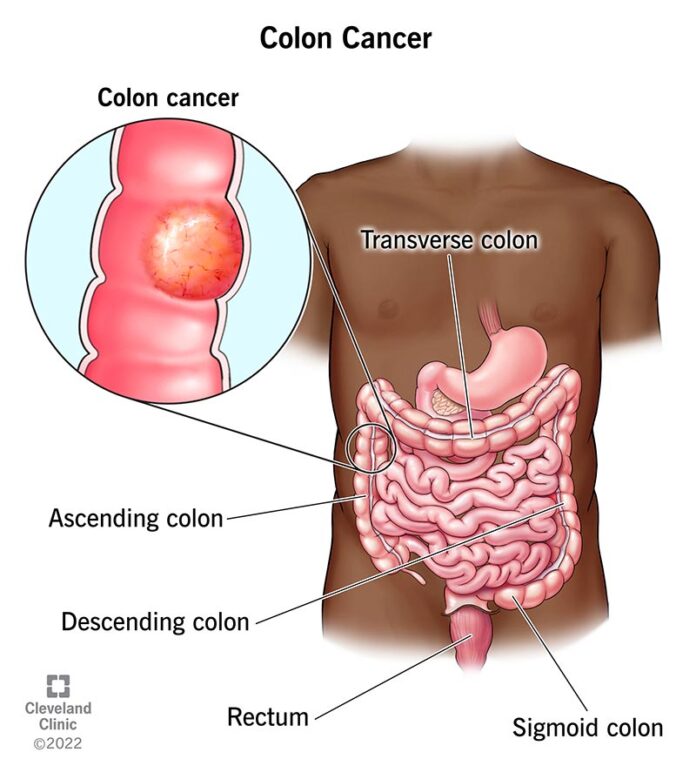
A growth of cells called colon cancer starts in the colon, a section of the large intestine. The first and longest segment of the big intestine is called the colon. The last segment of the digestive system is the large intestine. Food is broken down by the digestive system and used by the body.
Colon cancer can strike anyone at any age, but it usually strikes older persons. Usually, it starts off as little cell clusters inside the colon called polyps. Although most polyps are benign, some may eventually develop into colon cancer.
Polyps frequently show no symptoms. Doctors advise routine screening tests to check for colon polyps because of this. Polyp detection and removal aids in the prevention of colon cancer. Should colon cancer arise, numerous therapies can aid in its management. Among the treatments include radiation therapy, surgery, and medications like immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Symptoms
Many people with colon cancer don’t have symptoms at first. When symptoms appear, they’ll likely depend on the cancer’s size and where it is in the large intestine.
Symptoms of colon cancer can include:
- A change in bowel habits, such as more frequent diarrhoea or constipation.
- Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool.
- Ongoing discomfort in the belly area, such as cramps, gas or pain.
- A feeling that the bowel doesn’t empty all the way during a bowel movement.
- Weakness or tiredness.
- Losing weight without trying
Causes
What causes the majority of colon cancers is unknown to doctors.
When DNA alterations occur in colon cells, colon cancer results. The instructions that inform a cell what to do are encoded in its DNA. The alterations instruct the cells to proliferate rapidly. When healthy cells naturally die as part of their lifecycle, the modifications allow the cells to live on.
There are too many cells as a result. The cells may aggregate into a mass known as a tumour. Healthy bodily tissue can be invaded by the cells and destroyed. The cells may eventually separate and disperse to other areas of the body. Metastatic cancer is the term for cancer that spreads.
Factors at risk
The following are some factors that may raise your risk of colon cancer:
older years: Any age can develop colon cancer. However, the majority of colon cancer patients are over 50. The proportion of colon cancer cases in those under 50 has been rising. Physicians do not know why.
Black ethnicity: Compared to people of other races, black Americans are more likely to develop colon cancer.
a personal history of polyps or colorectal cancer. The risk of colon cancer is increased by prior colon cancer or colon polyps.
inflammation of the bowels. Inflammatory bowel illnesses, which are conditions that cause swelling and pain in the intestines, can raise the risk of colon cancer. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are two of these ailments.