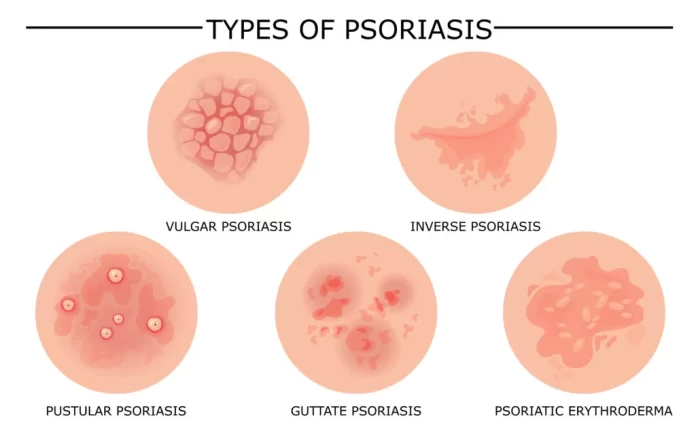
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin. It is characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, red, and scaly patches. It is not contagious, and its exact cause is not fully understood. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering an inflammatory response.
Symptoms:
- Red Patches: Raised, inflamed, and red patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales.
- Itching and Discomfort: The affected areas may be itchy, and individuals may experience discomfort or pain.
- Dry and Cracked Skin: The skin may become dry, and cracks may develop, leading to bleeding.
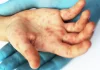
- Thickened Nails: It can affect the nails, causing thickening, pitting, and discoloration.
- Joint Pain: In some cases, psoriasis can also lead to joint pain, a condition known as psoriatic arthritis.
Causes:
- Genetic Factors: A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Immune System Dysfunction: It is considered an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors like stress, infections, and certain medications can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis.
- Inflammatory Response: Abnormal inflammation plays a key role in the development of psoriasis symptoms.
Treatment:
- Topical Treatments: Creams, ointments, and shampoos containing corticosteroids, retinoids, or other medications to reduce inflammation and scale formation.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can be beneficial in managing psoriasis symptoms.
- Systemic Medications: Oral or injectable medications that target the immune system to suppress the inflammatory response.
- Biologics: Specific drugs that target parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin moisturized can help alleviate dryness and reduce itching.
Prevention:
While psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle measures may help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups:
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate psoriasis, so stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga may be beneficial.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding specific triggers, such as certain medications or infections, can help prevent flare-ups.
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption may contribute to better overall health and potentially help managing it.
It’s important for individuals with psoriasis to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the severity of their condition and individual needs.